Effects of Pilates on inter-recti distance, thickness of rectus abdominis, waist circumference and abdominal muscle endurance in primiparous women
- PMID: 38008749
- PMCID: PMC10680311
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-023-02775-5
Effects of Pilates on inter-recti distance, thickness of rectus abdominis, waist circumference and abdominal muscle endurance in primiparous women
Abstract
Background: Pilates is expected to have a positive effect on women with weakened abdominal muscles after childbirth. Pilates may have a beneficial effect on the structure and function of the abdominal muscles in pregnant women. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate the effects of Pilates on inter-recti distance, thickness of the rectus abdominis, waist circumference, and abdominal muscle endurance in primiparous women.
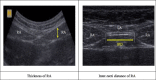
Methods: Thirty-five primiparous postpartum women were assigned to either the Pilates exercise group (n = 20) or the control group (n = 15). Pilates was undertaken by the exercise group for 50 min/day, 5 days/week, for 4 weeks. The control group maintained their daily activities without any intervention. The inter-recti distance was measured at three locations along the linea alba, and the thickness of the rectus abdominis was measured using ultrasound. Abdominal muscle endurance was measured using a repeated 1-min curl-up test. Waist circumference was also measured.
Results: The exercise group showed significant improvements from baseline in inter-recti distance, waist circumference, and abdominal muscle endurance (p < 0.05). The control group showed no significant improvement in these variables. Compared with the control group, the exercise group showed significantly improved performance in terms of inter-recti distance, waist circumference, and abdominal muscle endurance (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: The results of this study demonstrate that Pilates was effective in reducing inter-recti distance and waist circumference and improving abdominal muscle endurance in primiparous postpartum women. Pilates is considered an effective exercise for improving muscle structure and function in primiparous postpartum women, helping in the recovery from, and preventing, diastasis rectus abdominis.
Keywords: Diastasis rectus abdominis; Exercise; Primiparous; Rectus abdominis; Ultrasound.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Curl-up exercises improve abdominal muscle strength without worsening inter-recti distance in women with diastasis recti abdominis postpartum: a randomised controlled trial.J Physiother. 2023 Jul;69(3):160-167. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2023.05.017. Epub 2023 Jun 5. J Physiother. 2023. PMID: 37286390 Clinical Trial.
-
Acupuncture for postpartum diastasis recti abdominis and its effects on abdominal circumference, separation distance of rectus abdominis.Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2024 Feb 12;44(2):139-143. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20230626-k0004. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2024. PMID: 38373757 Clinical Trial. Chinese, English.
-
The Effect of Core Exercise Using Online Videoconferencing Platform and Offline-Based Intervention in Postpartum Woman with Diastasis Recti Abdominis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 8;19(12):7031. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127031. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35742279 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diagnostic techniques for diastasis recti.Hernia. 2021 Aug;25(4):915-919. doi: 10.1007/s10029-021-02469-7. Epub 2021 Jul 27. Hernia. 2021. PMID: 34313855 Review.
-
The effect of myofascial therapy on postpartum rectus abdominis separation, low back and leg pain, pelvic floor dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Nov 3;102(44):e35761. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035761. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37932976 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
#diastasisrecti: a mixed-methods analysis of Instagram posts and their influence on women's exercise and sports participation.BMC Womens Health. 2025 Jul 5;25(1):332. doi: 10.1186/s12905-025-03885-y. BMC Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 40618057 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Efficacy and Acceptability of Non-surgical Treatments with or without Exercise for Diastasis Recti Abdominis in Postpartum Women: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Sports Med. 2025 Apr;55(4):937-951. doi: 10.1007/s40279-025-02179-5. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 39878918
-
Comparison of Health Parameters in Postpartum Diastasis Recti: A Randomized Control Trial of SEMG Biofeedback-Assisted Core Strengthening Exercises with Kinesiotaping vs. Non-Assisted Exercises.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Aug 7;12(16):1567. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12161567. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39201126 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability of transversus abdominis thickness and inter-recti distance during forced expiration with limb adduction in primiparous women following vaginal delivery.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Mar 8;25(1):258. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07374-w. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40057695 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of conservative approaches for treating diastasis recti abdominis in postpartum women: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 6;104(23):e42723. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042723. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40489856 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- SR202106002/This study was supported by a grant by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism in South Korea
- SR202106002/This study was supported by a grant by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism in South Korea
- SR202106002/This study was supported by a grant by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism in South Korea
- SR202106002/This study was supported by a grant by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism in South Korea
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous