E3-ubiquitin ligase, FBXW7 regulates mitotic progression by targeting BubR1 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation
- PMID: 38008853
- PMCID: PMC11072012
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-023-05019-9
E3-ubiquitin ligase, FBXW7 regulates mitotic progression by targeting BubR1 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation
Abstract
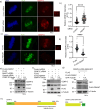
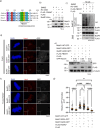
Faithful chromosome segregation requires correct attachment of kinetochores with the spindle microtubules. Erroneously-attached kinetochores recruit proteins to activate Spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), which senses the errors and signals cells to delay anaphase progression for error correction. Temporal control of the levels of SAC activating-proteins is critical for checkpoint activation and silencing, but its mechanism is not fully understood. Here, we show that E3 ubiquitin ligase, SCF-FBXW7 targets BubR1 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation and thereby controls SAC in human cells. Depletion of FBXW7 results in prolonged metaphase arrest with increased stabilization of BubR1 at kinetochores. Similar kinetochore stabilization is also observed for BubR1-interacting protein, CENP-E. FBXW7 induced ubiquitination of both BubR1 and the BubR1-interacting kinetochore-targeting domain of CENP-E, but CENP-E domain degradation is dependent on BubR1. Interestingly, Cdk1 inhibition disrupts FBXW7-mediated BubR1 targeting and further, phospho-resistant mutation of Cdk1-targeted phosphorylation site, Thr 620 impairs BubR1-FBXW7 interaction and FBXW7-mediated BubR1 ubiquitination, supporting its role as a phosphodegron for FBXW7. The results demonstrate SCF-FBXW7 as a key regulator of spindle assembly checkpoint that controls stability of BubR1 and its associated CENP-E at kinetochores. They also support that upstream Cdk1 specific BubR1 phosphorylation signals the ligase to activate the process.
Keywords: BubR1; CENP-E; Checkpoint; FBXW7; Kinetochore; Mitosis; SCF complex.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Bub1 and aurora B cooperate to maintain BubR1-mediated inhibition of APC/CCdc20.J Cell Sci. 2005 Aug 15;118(Pt 16):3639-52. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02487. Epub 2005 Jul 26. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16046481
-
The ubiquitin ligase FBXW7 targets the centriolar assembly protein HsSAS-6 for degradation and thereby regulates centriole duplication.J Biol Chem. 2020 Apr 3;295(14):4428-4437. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC119.012178. Epub 2020 Feb 21. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32086376 Free PMC article.
-
Human BUBR1 is a mitotic checkpoint kinase that monitors CENP-E functions at kinetochores and binds the cyclosome/APC.J Cell Biol. 1999 Sep 6;146(5):941-54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.146.5.941. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10477750 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress on spindle assembly checkpoint gene BubR1].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2011 Jul;40(4):446-50. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2011.04.018. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2011. PMID: 21845762 Review. Chinese.
-
Bub1 and BubR1: at the interface between chromosome attachment and the spindle checkpoint.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Aug;31(15):3085-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05326-11. Epub 2011 May 31. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21628528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
KIFC1 Overexpression Promotes Pancreatic Carcinoma Progression via Stabilising BUB1B.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Aug;29(16):e70767. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70767. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40857057 Free PMC article.
-
BubR1 and SIRT2: Insights into aneuploidy, aging, and cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2024 Nov;106-107:201-216. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2024.10.005. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Semin Cancer Biol. 2024. PMID: 39490401 Review.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Transiently Reversible Cell Vacuolization Caused by Excessive Serum Concentration in Scophthalmus maximus.Biology (Basel). 2024 Jul 19;13(7):545. doi: 10.3390/biology13070545. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056737 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

