Profiling Prokaryotic Communities and Aaptamines of Sponge Aaptos suberitoides from Tulamben, Bali
- PMID: 38008858
- PMCID: PMC11329227
- DOI: 10.1007/s10126-023-10268-7
Profiling Prokaryotic Communities and Aaptamines of Sponge Aaptos suberitoides from Tulamben, Bali
Abstract
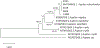
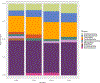
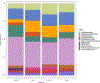
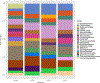
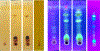
Sponges (Porifera) harbor a diversity of microorganisms that contribute largely to the production a vast array of bioactive compounds. The microorganisms associated with sponge have an important impact on the chemical diversity of the natural products. Herein, our study focuses on an Aaptos suberitoides commonly found in Indonesia. The objective of this study was to investigate the profile of prokaryotic community and the presence of aaptamine metabolites in sponge Aaptos suberitoides. Sponges were collected from two site locations (Liberty Wreck and Drop Off) in Tulamben, Bali. The sponges were identified by barcoding DNA cytochrome oxidase subunit I (COI) gene. The profile of prokaryotic composition was investigated by amplifying the 16S rRNA gene using primers 515f and 806r to target the V4 region. The metabolites were analyzed using LC-MS, and dereplication was done to identify the aaptamines and its derivates. The barcoding DNA of the sponges confirmed the identity of samples as Aaptos suberitoides. The prokaryotic communities of samples A. suberitoides were enriched and dominated by taxa Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi, Actinobacteria, and Acidobacteria. The chemical analysis showed that all sponges produce aaptamine and isoaaptamine except A. suberitoides S2421 produce analog of aaptamines. This is the first report on the profile of prokaryotic community and the aaptamine of tropical marine sponges, A. suberitoides, from Tulamben, Bali.
Keywords: Aaptamine; Aaptos suberitoides; Bali; Prokaryotic.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





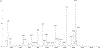


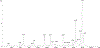

Similar articles
-
The Ethanol Extract of Marine Sponge Aaptos suberitoides Suppress Cell Viability, Cell Proliferation and Cell Migration in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Cell Line.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Feb 1;22(S1):25-32. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.S1.25. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 33576209
-
Aaptamine-rich Fraction from the Indonesian Marine Sponge, Aaptos suberitoides, Exhibits a Cytotoxic Effect on DLD-1 Colorectal Cancer Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 May 1;25(5):1737-1743. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.5.1737. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 38809646 Free PMC article.
-
Aaptamine derivatives from the Indonesian sponge Aaptos suberitoides.J Nat Prod. 2013 Jan 25;76(1):103-6. doi: 10.1021/np300794b. Epub 2013 Jan 2. J Nat Prod. 2013. PMID: 23282083
-
Review on marine sponge alkaloid, aaptamine: A potential antibacterial and anticancer drug.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022 Jan;99(1):103-110. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13932. Epub 2021 Aug 22. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022. PMID: 34331335 Review.
-
Chemical Ecology of Marine Sponges: New Opportunities through "-Omics".Integr Comp Biol. 2019 Oct 1;59(4):765-776. doi: 10.1093/icb/icz014. Integr Comp Biol. 2019. PMID: 30942859 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amelia TSM, Suaberon FAC, Vad J, Fahmi ADM, Saludes JP, Bhubalan K (2022) Recent advances of marine sponge-associated microorganisms as a source of commercially viable natural products. Mar Biotechnol 24:492–512 - PubMed
-
- Bibi F, Faheem M, Azhar EI, Yasir M, Alvi SA, Kamal MA, Ullah I, Naseer MI (2017) Bacteria from marine sponges: a source of new drugs. Curr Drug Metab 18:11–15 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
