Incidence and risk factors of post-stroke seizures and epilepsy: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38008901
- PMCID: PMC10683575
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605231213231
Incidence and risk factors of post-stroke seizures and epilepsy: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Due to variability in reports, the aim of this meta-analysis was to evaluate the incidence and risk factors of post-stroke early seizures (ES) and post-stroke epilepsy (PSE).
Methods: The MEDLINE, EMBASE and Web of Science databases were searched for post-stroke ES/PSE articles published on any date up to November 2020. Post-stroke ES included seizures occurring within 7 days of stroke, and PSE included at least one unprovoked seizure. Using random effects models, the incidence and risk factors of post-stroke ES and PSE were evaluated. The study was retrospectively registered with INPLASY (INPLASY2023100008).
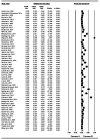
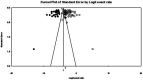
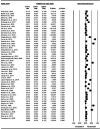
Results: Of 128 included studies in total, the incidence of post-stroke ES was 0.07 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.05, 0.10) and PSE was 0.10 (95% CI 0.08, 0.13). The rates were higher in children than adults. Risk factors for post-stroke ES included hemorrhagic stroke (odds ratio [OR] 2.14, 95% CI 1.44, 3.18), severe strokes (OR 2.68, 95% CI 1.73, 4.14), cortical involvement (OR 3.09, 95% CI 2.11, 4.51) and hemorrhagic transformation (OR 2.70, 95% CI 1.58, 4.60). Risk factors for PSE included severe strokes (OR 4.92, 95% CI 3.43, 7.06), cortical involvement (OR 3.20, 95% CI 2.13, 4.81), anterior circulation infarcts (OR 3.28, 95% CI 1.34, 8.03), hemorrhagic transformation (OR 2.81, 95% CI 1.25, 6.30) and post-stroke ES (OR 7.24, 95% CI 3.73, 14.06).
Conclusion: Understanding the risk factors of post-stroke ES/PSE may identify high-risk individuals who might benefit from prophylactic treatment.
Keywords: Epilepsy; hemorrhagic stroke; incidence; ischemic stroke; post-stroke; risk factors; seizures.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Seshadri S, Wolf PA. Lifetime risk of stroke and dementia: current concepts, and estimates from the Framingham Study. Lancet Neurol 2007; 6: 1106–1114. - PubMed
-
- Hauser WA, Annegers JF, Kurland LT. Incidence of epilepsy and unprovoked seizures in Rochester, Minnesota: 1935-1984. Epilepsia 1993; 34: 453–468. - PubMed
-
- Feyissa AM, Hasan TF, Meschia JF. Stroke-related epilepsy. Eur J Neurol 2019; 26: 18–e3. - PubMed
-
- Zelano J, Holtkamp M, Agarwal N, et al.. How to diagnose and treat post-stroke seizures and epilepsy. Epileptic Disord 2020; 22: 252–263. - PubMed
-
- Beghi E, Carpio A, Forsgren L, et al.. Recommendation for a definition of acute symptomatic seizure. Epilepsia 2010; 51: 671–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

