Oral administration of hyaluronic acid to improve skin conditions via a randomized double-blind clinical test
- PMID: 38009035
- PMCID: PMC10661223
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13531
Oral administration of hyaluronic acid to improve skin conditions via a randomized double-blind clinical test
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the impact of oral intake of Hyaluronic Acid (HA) on skin health.
Background: HA, an endogenous substance in the human body, plays a key role in skin health. However, its concentration in the skin decreases significantly with age. Previous studies suggested that oral intake of HA can supplement the body's HA level, but did not reveal the effects on different age groups and skin types.
Methods: A double-blind, randomized clinical trial with 129 female participants, covering young and elderly groups and differnet skin types, was conducted to assess the efficacy of orally administered HA on skin health.
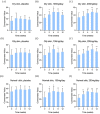
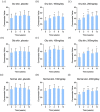
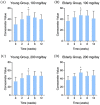
Results: Oral administration of HA significantly promoted skin hydration after 2-8 weeks among both young and elderly groups. Skin tone improvement was observed after 4-8 weeks, while an increase in epidermal thickness was noted after 12 weeks.
Conclusion: This study provides direct evidence supporting the clinical efficacy of oral intake of HA in promoting skin health.
Keywords: clinical benefit; hyaluronan; hyaluronic acid; oral administration; skin health.
© 2023 The Authors. Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of topical hyaluronic acid of different molecular weights in xerosis cutis treatment in elderly: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Jun 3;316(6):329. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03003-2. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 38829483 Clinical Trial.
-
Oral intake of a new full-spectrum hyaluronan improves skin profilometry and ageing: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.Eur J Dermatol. 2021 Dec 1;31(6):798-805. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2021.4176. Eur J Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34933842 Clinical Trial.
-
Ingested hyaluronan moisturizes dry skin.Nutr J. 2014 Jul 11;13:70. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-13-70. Nutr J. 2014. PMID: 25014997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Hyaluronan Relieves Wrinkles and Improves Dry Skin: A 12-Week Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Study.Nutrients. 2021 Jun 28;13(7):2220. doi: 10.3390/nu13072220. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34203487 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Hyaluronan in Barrier Alteration-Related Disease.Cells. 2021 Nov 9;10(11):3096. doi: 10.3390/cells10113096. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Life-Stage Approach to Precision Nutrition: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2024 Aug 13;16(8):e66813. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66813. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39144414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Animal Hyaluronic Acid and Probiotics Enhance Skin Health via the Gut-Skin Axis: An In Vitro Study on Bioavailability and Cellular Impact.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 22;26(3):897. doi: 10.3390/ijms26030897. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940667 Free PMC article.
-
Skin boosters: Definitions and varied classifications.Skin Res Technol. 2024 Mar;30(3):e13627. doi: 10.1111/srt.13627. Skin Res Technol. 2024. PMID: 38481069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photo-Crosslinked Pro-Angiogenic Hydrogel Dressing for Wound Healing.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 15;25(18):9948. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189948. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337435 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Collagen and Vitamin C and Their Combination with Hyaluronic Acid on Skin Density, Texture and Other Parameters: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 17;16(12):1908. doi: 10.3390/nu16121908. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38931263 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Fraser JR, Laurent TC, Laurent UB. Hyaluronan: its nature, distribution, functions and turnover. J Intern Med. 1997;242(1):27‐33. - PubMed
-
- Stern R, Asari AA, Sugahara KN. Hyaluronan fragments: an information‐rich system. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006;85(8):699‐715. - PubMed
-
- Zhang H, Cai W, Shao X. Regulation of aquaporin‐3 water permeability by hyaluronan. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2021;23(45):25706‐25711. - PubMed
-
- Sattar A, Rooney P, Kumar S, et al. Application of angiogenic oligosaccharides of hyaluronan increases blood vessel numbers in rat skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1994;103(4):576‐579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

