A novel hydrogel-based moisturizing cream composed of hyaluronic acid for patients with xerosis: An intraindividual comparative analysis
- PMID: 38009036
- PMCID: PMC10616540
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13499
A novel hydrogel-based moisturizing cream composed of hyaluronic acid for patients with xerosis: An intraindividual comparative analysis
Abstract
Background: Hyaluronic acid (HA) is mainly used to treat xerosis. It also exerts wound-healing, moisturizing, and antiaging effects. Although HA is considered an effective and safe ingredient in cosmetics, there is a constant demand for a more money-saving and effective formulation. This study aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a novel hydrogel-based moisturizer containing HA cross-linked with silicone polymers, produced solely through irradiation without the use of cross-linking agents.
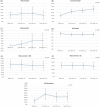
Materials and methods: A safety study enrolled 30 participants with healthy skin to perform patch and photopatch tests while recording adverse events. For the efficacy study, 30 participants with xerosis were compared before and after using the novel hydrogel, evaluating the cutaneous barrier function, xerosis severity scale (XSS) score, participant's satisfaction, and Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA). Furthermore, the efficacy of the novel hydrogel-based moisturizer was evaluated by comparing it with a conventional moisturizer, Physiogel, in another 30 participants with xerosis.
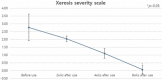
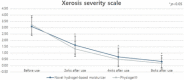
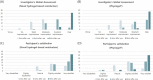
Results: In the safety study, no serious adverse events were observed. In the efficacy study before and after use, skin hydration and skin surface lipid increased (p < 0.05) whereas the XSS scores decreased (p < 0.05) with time. In the comparative efficacy study with Physiogel, skin hydration increased whereas the XSS scores decreased (p < 0.05) over time in both groups. Furthermore, IGA improved in 100% of participants in both groups. Also, 100% and 93% of participants were satisfied with the novel hydrogel-based moisturizer and Physiogel, respectively.
Conclusions: The novel hydrogel-based moisturizer proved to be safe and effective for xerosis, showing comparable results to the conventional moisturizer.
Keywords: efficacy; hyaluronic acid; moisturizer; safety; xerosis.
© 2023 The Authors. Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Safety and efficacy of a new hydrogel based on hyaluronic acid as cosmeceutical for xerosis.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022 Dec;21(12):6840-6849. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15368. Epub 2022 Sep 20. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 36074117
-
The 24-hr, 28-day, and 7-day post-moisturizing efficacy of ceramides 1, 3, 6-II containing moisturizing cream compared with hydrophilic cream on skin dryness and barrier disruption in senile xerosis treatment.Dermatol Ther. 2019 Nov;32(6):e13090. doi: 10.1111/dth.13090. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Dermatol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31585489 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of anti-inflammatory moisturizer vs hydrophilic cream in elderly patients with moderate to severe xerosis: A split site, triple-blinded, randomized, controlled trial.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020 Jun;19(6):1432-1438. doi: 10.1111/jocd.13183. Epub 2019 Oct 14. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31609077 Clinical Trial.
-
Modern moisturizer myths, misconceptions, and truths.Cutis. 2013 Jun;91(6):308-14. Cutis. 2013. PMID: 23837155 Review.
-
Efficacy of moisturizers in paediatric atopic dermatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021 Jan-Feb;88(1):22-31. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_1384_20. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021. PMID: 34623061
Cited by
-
HSPiP and QbD oriented optimized stearylamine-elastic liposomes for topical delivery of ketoconazole to treat deep seated fungal infections: In vitro and ex vivo evaluations.Int J Pharm X. 2024 Aug 26;8:100279. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2024.100279. eCollection 2024 Dec. Int J Pharm X. 2024. PMID: 39282055 Free PMC article.
-
Prinsepia utilis Royle polysaccharides promote skin barrier repair through the Claudin family.Skin Res Technol. 2024 Jul;30(7):e13848. doi: 10.1111/srt.13848. Skin Res Technol. 2024. PMID: 38978226 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogel-Based Continuum Soft Robots.Gels. 2025 Mar 27;11(4):254. doi: 10.3390/gels11040254. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40277689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- White‐Chu EF, Reddy M. Dry skin in the elderly: complexities of a common problem. Clin Dermatol. 2011;29:37‐42. - PubMed
-
- Farage MA, Miller KW, Berardesca E, et al. Clinical implications of aging skin: cutaneous disorders in the elderly. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2009;10:73‐86. - PubMed
-
- Rawlings AV, Watkinson A, Rogers J, Mayo A‐M, Hope J. Abnormalities in stratum corneum structure, lipid composition, and desmosome degradation in soap‐induced winter xerosis. J Soc Cosmet Chem. 1994;45:203‐220.
-
- Hahnel E, Lichterfeld A, Blume‐Peytavi U, Kottner J. The epidemiology of skin conditions in the aged: a systematic review. J Tissue Viability. 2017;26:20‐28. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

