A Virtual Reality Exergame: Clinician-Guided Breathing and Relaxation for Children with Muscular Dystrophy
- PMID: 38009078
- PMCID: PMC10676767
- DOI: 10.1109/vrw58643.2023.00065
A Virtual Reality Exergame: Clinician-Guided Breathing and Relaxation for Children with Muscular Dystrophy
Abstract
This study introduces a VR-based breathing and relaxation exergame tailored for individuals with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). DMD is a rare neuromuscular disease that leads to respiratory muscle dysfunction with anxiety being a common comorbidity. Clinical management requires frequent visits to rare disease specialists to manage symptom progression. Limited availability and/or proximity of rare disease experts present challenges to care and can lead to missed care opportunities and reduced quality of life. We propose a breathing and relaxation exergame with remote telehealth applicability that incorporates shared patient-clinician VR interaction, and physiological sensors that provide both real-time feedback to the patient and health analytics for the clinician. The game focuses on two key aspects of DMD clinical care that can be mediated through control of breathing: relaxation/mindfulness training and respiratory muscle exercise. The system was evaluated among 13 individuals, including 4 participants with DMD. Feedback surveys, interviews, and focus group discussions with participants, accompanying family members, and clinicians demonstrated the feasibility of this VR tool for telehealth or as part of a home exercise program.
Keywords: Human computer interaction (HCI); Human-centered computing; Interaction paradigms; Telehealth; VR Mindfulness; VR Rehabilitation; Virtual reality.
Figures
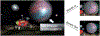


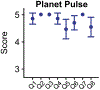
References
-
- Rare diseases,” National Institutes of Health, 11-Feb-2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.nih.gov/about-nih/what-we-do/nih-turning-discovery-into-heal....
-
- Richter T, Nestler-Parr S, Babela R, Khan ZM, Tesoro T, Molsen E, and Hughes DA, “Rare disease terminology and definitions—a systematic global review: Report of the ispor rare disease special interest group,” Value in Health, vol. 18, no. 6, pp. 906–914, 2015. - PubMed
-
- “What is muscular dystrophy?,” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,21-Nov-2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/musculardystrophy/facts.html.
-
- “What are the types and symptoms of muscular dystrophy (MD)?,” Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. [Online]. Available: https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/musculardys/conditioninfo/types.
-
- Sobierajska-Rek A, Mański Ł, Jabłońska-Brudło J, Śledzińska K, Wasilewska E, and Szalewska D, “Respiratory telerehabilitation of boys and young men with Duchenne muscular dystrophy in the COVID-19 pandemic,” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, vol. 18, no. 12, p. 6179, 2021. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
