LINC01140 Hinders the Development of Breast Cancer Through Targeting miR-200b-3p to Downregulate DMD
- PMID: 38009192
- PMCID: PMC10683380
- DOI: 10.1177/09636897231211202
LINC01140 Hinders the Development of Breast Cancer Through Targeting miR-200b-3p to Downregulate DMD
Abstract
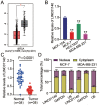
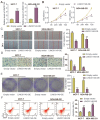
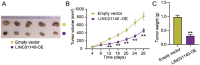
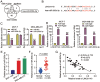
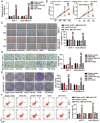
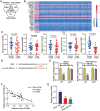
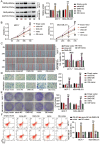
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are frequently reported to be involved in breast cancer (BC) oncogenicity. The goal of this study was to probe lncRNA LINC01140's role and action mechanism in BC. Relative LINC01140, miR-200b-3p, and dystrophin (DMD) levels were determined using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). DMD protein levels in BC cells were quantified using Western blotting, and the targeting relationships were validated by luciferase reporter assays and RNA immunoprecipitation experiments. The proliferative potential of the cells was evaluated using CCK-8 and colony formation tests, while the migratory and invasive abilities of the cells were assessed using scratch and transwell assays. Apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry. Nude mouse models have been established to allow the examination of tumor growth in vivo. Pronounced downregulation of LINC01140 and DMD, as well as upregulation of miR-200b-3p, was observed in BC. LINC01140 binds directly to miR-200b-3p to downregulate DMD expression. Ectopic LINC01140 expression not only limited tumor growth in vivo but also diminished the proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities of BC cells in vitro, however, it induced apoptosis in BC cells. Elevated miR-200b-3p expression stimulated the tumorigenic potential of BC cells and attenuated the suppressive effect of LINC01140 or DMD overexpression on BC cell malignancy, whereas DMD overexpression restricted the tumorigenic potential of BC cells. Overall, LINC01140 prevents BC development via the miR-200b-3p-DMD axis. These findings support the latent potential and usefulness of the LINC01140-miR-200b-3p-DMD network as a target for BC therapy.
Keywords: DMD; LINC01140; breast cancer; lncRNA; miR-200b-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Rossi S, Schinzari G, Basso M, Strippoli A, Dadduzio V, D’Argento E, Cassano A, Barone C. Maintenance hormonal and chemotherapy treatment in metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review. Future Oncol. 2016;12(10):1299–307. - PubMed
-
- Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, Barregard L, Bhutta ZA, Brenner H, Dicker DJ, Chimed-Orchir O, Dandona R, Dandona L, Fleming T, et al.. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups,1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(4):524–48. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):9–29. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

