Targeting the mechano-microenvironment and liver cancer stem cells: a promising therapeutic strategy for liver cancer
- PMID: 38009775
- PMCID: PMC10690881
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2023.0229
Targeting the mechano-microenvironment and liver cancer stem cells: a promising therapeutic strategy for liver cancer
Abstract
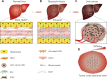
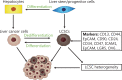
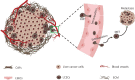
Over the past 2 decades, cancer stem cells (CSCs) have been identified as the root cause of cancer occurrence, progression, chemoradioresistance, recurrence, and metastasis. Targeting CSCs is a novel therapeutic strategy for cancer management and treatment. Liver cancer (LC) is a malignant disease that can endanger human health. Studies are increasingly suggesting that changes in the liver mechanical microenvironment are a primary driver triggering the occurrence and development of liver cancer. In this review, we summarize current understanding of the roles of the liver mechano-microenvironment and liver cancer stem cells (LCSCs) in liver cancer progression. We also discuss the relationship between the mechanical heterogeneity of liver cancer tissues and LCSC recruitment and metastasis. Finally, we highlight potential mechanosensitive molecules in LCSCs and mechanotherapy in liver cancer. Understanding the roles and regulatory mechanisms of the mechano-microenvironment and LCSCs may provide fundamental insights into liver cancer progression and aid in further development of novel therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Liver cancer; cancer stem cells; mechano-microenvironment; mechanotherapy; tumor heterogeneity.
Copyright © 2023 Cancer Biology & Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cancer Stem Cell Functions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies.Cells. 2020 May 26;9(6):1331. doi: 10.3390/cells9061331. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32466488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone demethylase JMJD2D promotes the self-renewal of liver cancer stem-like cells by enhancing EpCAM and Sox9 expression.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100121. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015335. Epub 2020 Dec 3. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33434575 Free PMC article.
-
[Novel therapeutic strategies for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: targeting intervention on liver cancer stem cells].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Aug;30(4):894-8. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24059077 Review. Chinese.
-
Targeting cancer stem cells as a therapeutic approach in liver cancer.Curr Gene Ther. 2015;15(2):161-70. doi: 10.2174/1566523214666141224095938. Curr Gene Ther. 2015. PMID: 25537770 Review.
-
Cancer stem cell-immune cell crosstalk in the tumor microenvironment for liver cancer progression.Front Med. 2024 Jun;18(3):430-445. doi: 10.1007/s11684-023-1049-z. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Front Med. 2024. PMID: 38600350 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of continuous infusion chemotherapy through femoral artery catheterization on GP73, AFP-L3, and safety efficacy in liver cancer patients.Clin Exp Med. 2025 May 10;25(1):148. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01560-y. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40347395 Free PMC article.
-
Intricate effects of post-translational modifications in liver cancer: mechanisms to clinical applications.J Transl Med. 2024 Jul 13;22(1):651. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05455-6. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38997696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ABCA1 promote tumor environment heterogeneity via epithelial mesenchymal transition in Huh7 and HepG2 liver cancer cell.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 19;15:1498528. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1498528. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39749197 Free PMC article.
-
The dual role of autophagy in cancer stem cells: implications for tumor progression and therapy resistance.J Transl Med. 2025 May 25;23(1):583. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06595-z. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40414839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Progress of Liver Cancer Recurrence Based on Energy Metabolism of Liver Cancer Stem Cells.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025 Mar 3;12:467-480. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S500638. eCollection 2025. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2025. PMID: 40061164 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Weiderpass E, Soerjomataram I. The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer. 2021;127:3029–30. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Parkin DM, Piñeros M, Znaor A, et al. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: an overview. Int J cancer. 2021;149:778–89. - PubMed
-
- You Z, Zhou L, Li W, Huang C, Du Y. Mechanical microenvironment as a key cellular regulator in the liver. Acta Mech Sin. 2019;35:289–98.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
