Development of a novel streamlined workflow (AACRE) and database (inCREDBle) for genomic analysis of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales
- PMID: 38010338
- PMCID: PMC10711315
- DOI: 10.1099/mgen.0.001132
Development of a novel streamlined workflow (AACRE) and database (inCREDBle) for genomic analysis of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales
Abstract
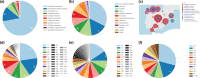
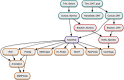
In response to the threat of increasing antimicrobial resistance, we must increase the amount of available high-quality genomic data gathered on antibiotic-resistant bacteria. To this end, we developed an integrated pipeline for high-throughput long-read sequencing, assembly, annotation and analysis of bacterial isolates and used it to generate a large genomic data set of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CPE) isolates collected in Spain. The set of 461 isolates were sequenced with a combination of both Illumina and Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) DNA sequencing technologies in order to provide genomic context for chromosomal loci and, most importantly, structural resolution of plasmids, important determinants for transmission of antimicrobial resistance. We developed an informatics pipeline called Assembly and Annotation of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae (AACRE) for the full assembly and annotation of the bacterial genomes and their complement of plasmids. To explore the resulting genomic data set, we developed a new database called inCREDBle that not only stores the genomic data, but provides unique ways to filter and compare data, enabling comparative genomic analyses at the level of chromosomes, plasmids and individual genes. We identified a new sequence type, ST5000, and discovered a genomic locus unique to ST15 that may be linked to its increased spread in the population. In addition to our major objective of generating a large regional data set, we took the opportunity to compare the effects of sample quality and sequencing methods, including R9 versus R10 nanopore chemistry, on genome assembly and annotation quality. We conclude that converting short-read and hybrid microbial sequencing and assembly workflows to the latest nanopore chemistry will further reduce processing time and cost, truly enabling the routine monitoring of resistance transmission patterns at the resolution of complete chromosomes and plasmids.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales; database; genome assembly; nanopore sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
F.B. and M.A.-T. are Roche employees, and the work was partly funded by Roche.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparing antimicrobial resistant genes and phenotypes across multiple sequencing platforms and assays for Enterobacterales clinical isolates.BMC Microbiol. 2023 Aug 18;23(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02975-x. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37596530 Free PMC article.
-
Applying Rapid Whole-Genome Sequencing To Predict Phenotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Results among Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Dec 21;63(1):e01923-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01923-18. Print 2019 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 30373801 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking of Antibiotic Resistance Transfer and Rapid Plasmid Evolution in a Hospital Setting by Nanopore Sequencing.mSphere. 2020 Aug 19;5(4):e00525-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00525-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32817379 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of R9.4.1/Kit10 and R10/Kit12 Oxford Nanopore flowcells and chemistries in bacterial genome reconstruction.Microb Genom. 2023 Jan;9(1):mgen000910. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000910. Microb Genom. 2023. PMID: 36748454 Free PMC article.
-
The rapid spread of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae.Drug Resist Updat. 2016 Nov;29:30-46. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Drug Resist Updat. 2016. PMID: 27912842 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Global action plan on antimicrobial resistance. [ October 21; 2020 ]. https://www.who.int/antimicrobial-resistance/publications/global-action-... n.d. accessed.
-
- WHO Global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to guide research, discovery, and development of new antibiotics. [ October 21; 2020 ]. https://www.who.int/medicines/publications/global-priority-list-antibiot... n.d. accessed.
-
- Cassini A, Högberg LD, Plachouras D, Quattrocchi A, Hoxha A, et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: a population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019;19:56–66. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30605-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

