RsaM: a unique dominant regulator of AHL quorum sensing in bacteria
- PMID: 38010341
- PMCID: PMC10710839
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.001417
RsaM: a unique dominant regulator of AHL quorum sensing in bacteria
Abstract
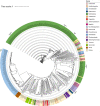
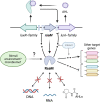
Quorum sensing (QS) in proteobacteria is a mechanism to control gene expression orchestrated by the LuxI/LuxR protein family pair, which produces and responds to N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) diffusible signal molecules. QS is often regarded as a cell density response via the sensing of/response to the concentrations of AHLs, which are constantly basally produced by bacterial cells. The luxI/R systems, however, undergo supra-regulation in response to external stimuli and many regulators have been implicated in controlling QS in bacteria, although it remains unclear how most of these regulators and cues contribute to the QS response. One regulator, called RsaM, has been reported in a few proteobacterial species to have a stringent role in the control of AHL QS. RsaMs are small, in the range of 140-170 aa long, and are found in several genera, principally in Burkholderia and Acinetobacter. The gene encoding RsaM is always located as an independent transcriptional unit, situated adjacent to QS luxI and/or luxR loci. One of the most remarkable aspects of RsaM is its uniqueness; it does not fall into any of the known bacterial regulatory families and it possesses a distinct and novel fold that does not exhibit binding affinity for nucleic acids or AHLs. RsaM stands out as a distinctive regulator in bacteria, as it is likely to have an important ecological role, as well as unravelling a novel way of gene regulation in bacteria.
Keywords: AHL; LuxI/R; RsaM; bacteria; quorum sensing; regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Mesorhizobium japonicum quorum sensing circuit that involves three linked genes and an unusual acyl-homoserine lactone signal.mBio. 2023 Aug 31;14(4):e0101023. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01010-23. Epub 2023 May 25. mBio. 2023. PMID: 37227303 Free PMC article.
-
An evolving perspective on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa orphan quorum sensing regulator QscR.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Oct 28;4:152. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00152. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25389523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The atypical organization of the luxI/R family genes in AHL-driven quorum-sensing circuits.J Bacteriol. 2024 Feb 22;206(2):e0043023. doi: 10.1128/jb.00430-23. Epub 2024 Jan 19. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38240569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two rsaM Homologues Encode Central Regulatory Elements Modulating Quorum Sensing in Burkholderia thailandensis.J Bacteriol. 2018 Jun 25;200(14):e00727-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00727-17. Print 2018 Jul 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29507087 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of a LuxI/R-type quorum sensing system in Pseudoalteromonas.Res Microbiol. 2019 Sep-Oct;170(6-7):243-255. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2019.07.001. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Res Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31325485
Cited by
-
Pseudomonas fuscovaginae quorum sensing studies: 5% dominates cell-to-cell conversations.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 May 2;12(5):e0417923. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04179-23. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38511955 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

