Epitope mapping of monoclonal antibodies: a comprehensive comparison of different technologies
- PMID: 38010385
- PMCID: PMC10730160
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2023.2285285
Epitope mapping of monoclonal antibodies: a comprehensive comparison of different technologies
Abstract
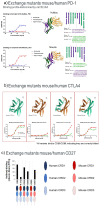
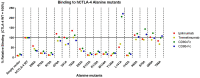
Monoclonal antibodies have become an important class of therapeutics in the last 30 years. Because the mechanism of action of therapeutic antibodies is intimately linked to their binding epitopes, identification of the epitope of an antibody to the antigen plays a central role during antibody drug development. The gold standard of epitope mapping, X-ray crystallography, requires a high degree of proficiency with no guarantee of success. Here, we evaluated six widely used alternative methods for epitope identification (peptide array, alanine scan, domain exchange, hydrogen-deuterium exchange, chemical cross-linking, and hydroxyl radical footprinting) in five antibody-antigen combinations (pembrolizumab+PD1, nivolumab+PD1, ipilimumab+CTLA4, tremelimumab+CTLA4, and MK-5890+CD27). The advantages and disadvantages of each technique are demonstrated by our data and practical advice on when and how to apply specific epitope mapping techniques during the drug development process is provided. Our results suggest chemical cross-linking most accurately identifies the epitope as defined by crystallography.
Keywords: Alanine scan; Epitope mapping; Hydrogen deuterium exchange; cross-linking; hydroxyl radical footprinting; monoclonal antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
D.L. Hulsik and J. Kreijtz are employed by, and may own stock in, Aduro Biotech Europe who partially provided funding for this study and own stock in Chinook Therapeutics (KDNY). A. Beebe, X. Dang, M. Beaumont, E. Hsieh, G. Ermacov, T. Fischmann, and V. Juan, are employed by, and may own stock in, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, who partially provided funding for this study. A. Nazabal is employed by, and may own stock in, CovalX. Inc, who provided chemical cross-linking data for this study. L. Guelen and H.v. Eenennaam hold patents in Merck Sharpe & Dohme Corp and own Chinook stock.
Figures
References
-
- Sukumar S, Wilson DC, Yu Y, Wong J, Naravula S, Ermakov G, Riener R, Bhagwat B, Necheva AS, Grein J, et al. Characterization of MK-4166, a clinical agonistic antibody that targets human GITR and inhibits the generation and suppressive effects of T regulatory cells. Cancer Res. 2017;77(16):4378–88. 1439.2016. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1439. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Meerten T, Rozemuller H, Hol S, Moerer P, Zwart M, Hagenbeek A, Mackus WJM, Parren PWHI, van de Winkel JGJ, Ebeling SB, et al. HuMab-7D8, a monoclonal antibody directed against the membrane-proximal small loop epitope of CD20 can effectively eliminate CD20low expressing tumor cells that resist Rituximab mediated lysis. Haematologica. 2010;95(12):2063–71. haematol.2010.025783. doi:10.3324/haematol.2010.025783. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- He W, Tan GS, Mullarkey CE, Lee AJ, Lam MMW, Krammer F, Henry C, Wilson PC, Ashkar AA, Palese P, et al. Epitope specificity plays a critical role in regulating antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against influenza A virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113(42):11931. doi:10.1073/pnas.1609316113. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials