The effect of levetiracetam on depression and anti-oxidant activity in patients with epilepsy
- PMID: 38011345
- PMCID: PMC10189196
- DOI: 10.18502/cjn.v21i4.11719
The effect of levetiracetam on depression and anti-oxidant activity in patients with epilepsy
Abstract
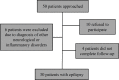
Background: Levetiracetam (LEV) is approved for treating epilepsy. The current evidence shows that LEV can cause behavioral problems such as depression. It is well-known that depression is associated with oxidative stress. Therefore, we conducted this study to assess the influence of LEV on depression severity and anti-oxidant status. Methods: In this prospective longitudinal study, 50 patients with diagnosis of epilepsy on LEV were included. We used Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) to assess depression severity. The serum levels of zinc and glutathione were measured as anti-oxidant markers. These variables were evaluated at the baseline and 3 months after the commencement of LEV. Results: A total of 30 patients finished the follow-up. Among them, 21 patients were women. The mean age at baseline was 28.76 ± 11.37 (range: 16-68 years). The severity of depression at the last follow-up was significantly higher than the baseline. We observed a decrease in the serum levels of zinc and glutathione, though they were not statistically significant. Conclusion: Our results suggest that LEV can increase the risk of depression in patients with epilepsy. This study also suggests that zinc depletion can be induced through act of LEV. Further studies are needed to validate these findings.
Keywords: Depression; Epilepsy; Glutathione; Oxidative Stress; Zinc.
Copyright © 2022 Iranian Neurological Association, and Tehran University of Medical Sciences Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest in this study.
References
-
- Sills GJ, Rogawski MA. Mechanisms of action of currently used antiseizure drugs. Neuropharmacology. 2020;168:107966. - PubMed
-
- Marson A, Burnside G, Appleton R, Smith D, Leach JP, Sills G, et al. The SANAD II study of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of levetiracetam, zonisamide, or lamotrigine for newly diagnosed focal epilepsy: An open-label, non-inferiority, multicentre, phase 4, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2021;397(10282):1363–74. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee SK, Lee SA, Kim DW, Loesch C, Pelgrims B, Osakabe T, et al. A randomized, open-label, multicenter comparative trial of levetiracetam and topiramate as adjunctive treatment for patients with focal epilepsy in Korea. Epilepsy Behav. 2019;97:67–74. - PubMed
-
- Steinhoff BJ, Klein P, Klitgaard H, Laloyaux C, Moseley BD, Ricchetti-Masterson K, et al. Behavioral adverse events with brivaracetam, levetiracetam, perampanel, and topiramate: A systematic review. Epilepsy Behav. 2021;118:107939. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources