Glue ablation of Rasmussen's aneurysm in a case of epituberculosis
- PMID: 38011962
- PMCID: PMC10685935
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2022-253372
Glue ablation of Rasmussen's aneurysm in a case of epituberculosis
Abstract
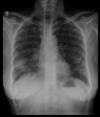
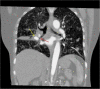
A woman in her 40s presented with massive haemoptysis and breathlessness for 1 day. She had been diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis based on sputum CBNAAT (Cartridge Based Nucleic Acid Amplification Test) and was on antitubercular treatment for previous 2 weeks. Her chest X-ray showed right middle lobe lateral segment dense consolidation with bilateral nodular infiltrates. CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) revealed a well-defined homogenously enhancing vascular lesion of size 10×11×13 mm in the right hilar region communicating with the descending branch of right pulmonary artery, suggesting a Rasmussen's aneurysm. It was in close proximity to the segmental bronchus that was almost completely occluded, suggesting epituberculosis. Transvenous pulmonary artery glue embolisation successfully achieved complete ablation of the aneurysm with preserved arterial flow. She has later completed 6 months of antitubercular treatment and is cured with no recurrence of haemoptysis. Her lung infiltrates have resolved with some lung scarring.
Keywords: Interventional radiology; Respiratory system; TB and other respiratory infections; Tuberculosis.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2023. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
