Delineation of DNA and mRNA COVID-19 vaccine-induced immune responses in preclinical animal models
- PMID: 38012018
- PMCID: PMC10760386
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2281733
Delineation of DNA and mRNA COVID-19 vaccine-induced immune responses in preclinical animal models
Abstract
Nucleic acid vaccines are designed based on genetic sequences (DNA or mRNA) of a target antigen to be expressed in vivo to drive a host immune response. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, mRNA and DNA vaccines based on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike antigen were developed. Surprisingly, head-to-head characterizations of the immune responses elicited by each vaccine type has not been performed to date. Here, we have employed a range of preclinical animal models including the hamster, guinea pig, rabbit, and mouse to compare and delineate the immune response raised by DNA, administered intradermally (ID) with electroporation (EP) and mRNA vaccines (BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273), administered intramuscularly (IM), expressing the SARS-CoV-2 WT spike antigen. The results revealed clear differences in the quality and magnitude of the immune response between the two vaccine platforms. The DNA vaccine immune response was characterized by strong T cell responses, while the mRNA vaccine elicited robust humoral responses. The results may assist in guiding the disease target each vaccine type may be best matched against and suggest mechanisms to further enhance the breadth of each platform's immune response.
Keywords: COVID-19; DNA vaccines; SARS-CoV-2; animal models; immunogenicity; mRNA vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
VMA, IM, RK, LJ, OB, LH, and TRFS are employees of and may hold stock options in Inovio Pharmaceuticals., Inc. DWK is the recipient of research funding from Inovio Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Figures
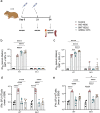
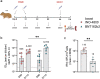
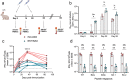
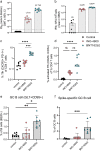
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
