Complex 33-beam simulated galactic cosmic radiation exposure impacts cognitive function and prefrontal cortex neurotransmitter networks in male mice
- PMID: 38012180
- PMCID: PMC10682413
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42173-x
Complex 33-beam simulated galactic cosmic radiation exposure impacts cognitive function and prefrontal cortex neurotransmitter networks in male mice
Abstract
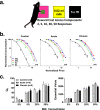
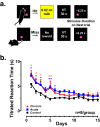
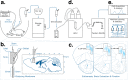
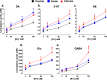
Astronauts will encounter extended exposure to galactic cosmic radiation (GCR) during deep space exploration, which could impair brain function. Here, we report that in male mice, acute or chronic GCR exposure did not modify reward sensitivity but did adversely affect attentional processes and increased reaction times. Potassium (K+)-stimulation in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) elevated dopamine (DA) but abolished temporal DA responsiveness after acute and chronic GCR exposure. Unlike acute GCR, chronic GCR increased levels of all other neurotransmitters, with differences evident between groups after higher K+-stimulation. Correlational and machine learning analysis showed that acute and chronic GCR exposure differentially reorganized the connection strength and causation of DA and other PFC neurotransmitter networks compared to controls which may explain space radiation-induced neurocognitive deficits.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The longitudinal behavioral effects of acute exposure to galactic cosmic radiation in female C57BL/6J mice: Implications for deep space missions, female crews, and potential antioxidant countermeasures.J Neurochem. 2025 Jan;169(1):e16225. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16225. Epub 2024 Sep 25. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 39318241 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a 33-ion sequential beam galactic cosmic ray analog on male mouse behavior and evaluation of CDDO-EA as a radiation countermeasure.Behav Brain Res. 2022 Feb 15;419:113677. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113677. Epub 2021 Nov 21. Behav Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 34818568 Free PMC article.
-
Life-long brain compensatory responses to galactic cosmic radiation exposure.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 22;11(1):4292. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83447-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33619310 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia: Ally and Enemy in Deep Space.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Jul;126:509-514. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.03.036. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 33862064 Review.
-
Getting ready for the manned mission to Mars: the astronauts' risk from space radiation.Naturwissenschaften. 2007 Jul;94(7):517-26. doi: 10.1007/s00114-006-0204-0. Epub 2007 Jan 19. Naturwissenschaften. 2007. PMID: 17235598 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term, Sex-Specific Effects of GCRsim and Gamma Irradiation on the Brains, Hearts, and Kidneys of Mice with Alzheimer's Disease Mutations.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 16;25(16):8948. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168948. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201636 Free PMC article.
-
The longitudinal behavioral effects of acute exposure to galactic cosmic radiation in female C57BL/6J mice: Implications for deep space missions, female crews, and potential antioxidant countermeasures.J Neurochem. 2025 Jan;169(1):e16225. doi: 10.1111/jnc.16225. Epub 2024 Sep 25. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 39318241 Free PMC article.
-
A second space age spanning omics, platforms and medicine across orbits.Nature. 2024 Aug;632(8027):995-1008. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07586-8. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38862027 Review.
References
-
- Saganti PB, Cucinotta FA, Wilson JW, Simonsen LC, Zeitlin C. Radiation climate map for analyzing risks to astronauts on the Mars surface from galactic cosmic rays. Space Sci. Rev. 2004;110:143–156. doi: 10.1023/B:SPAC.0000021010.20082.1a. - DOI
-
- Yasuda H, Komiyama T, Fujitaka K. Probability of hippocampus cell hits by high-LET space radiation in a low-Earth orbit mission (STS-91) Phys. Med. 2001;17:166–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

