The mediating role of healthy lifestyle behavior in the relationship between religious practice and academic achievement in university students
- PMID: 38012783
- PMCID: PMC10683229
- DOI: 10.1186/s40359-023-01455-1
The mediating role of healthy lifestyle behavior in the relationship between religious practice and academic achievement in university students
Abstract
Background: The issues of religious practice, healthy lifestyle behavior and academic achievement are global agendas. Most previous research has focused on either one or two of the variables, not three of them (e.g. just the relationship between religious practice and healthy lifestyle behavior). And addressing these three issues, by and large, demands a systemic approach to re-thinking the current level and improving it.
Objective: To examine the causal relationship between religious practice, healthy lifestyle behavior, and academic achievement in the case of Debre Markos University (DMU) and Injibara University (IU), Ethiopia.
Methods: Four hundred forty students are participated voluntarily using random sampling techniques. To attain this objective, a cross-sectional research method design was used.
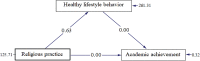
Results: The mean scores of students' healthy lifestyle behavior is more than average in all aspects. MANOVA results revealed that batch, ethnicity (region), and the university did not display a statistically significant difference among the composite (or combined) scores of both students' healthy lifestyles and religious practice. However, religious affiliation and gender religious practice and have an effect on religious practice and healthy lifestyle behavior respectively. The correlation output informs that religious practice and healthy lifestyle behavior are positively and significantly correlated with each other. Religious practice also significantly predicted students' healthy lifestyle behavior. Despite this, the academic achievement of students didn't have any relationship with their religious practice and healthy lifestyle behavior.
Conclusion: University students' healthy lifestyle behavior doesn't play an intervening variable in the effect of religious practice on academic achievement. Possible practical implications and recommendations have been forwarded.
Keywords: Academic achievement; Healthy lifestyle behavior; Religious practice; University students.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anesthesia students' perception of the educational environment and academic achievement at Debre Tabor University and University of Gondar, Ethiopia: a comparative cross-sectional study.BMC Med Educ. 2022 Jul 15;22(1):552. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03611-4. BMC Med Educ. 2022. PMID: 35840966 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the effects of health behaviors and mental health on students' academic achievement: a cross-sectional study on lebanese university students.BMC Public Health. 2023 Jun 26;23(1):1228. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16184-8. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37365573 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Intelligence and Pro-Social Behavior as Predictors of Academic Achievement Among University Students.Community Health Equity Res Policy. 2023 Jul;43(4):431-441. doi: 10.1177/0272684X211033447. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Community Health Equity Res Policy. 2023. PMID: 34325558
-
Influence of psychological hardiness on academic achievement of university students: The mediating effect of academic engagement.Work. 2023;74(4):1515-1525. doi: 10.3233/WOR-211358. Work. 2023. PMID: 36565087
-
Circadian preference and academic achievement in school-aged students: a systematic review and a longitudinal investigation of reciprocal relations.Chronobiol Int. 2021 Aug;38(8):1195-1214. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2021.1921788. Epub 2021 May 13. Chronobiol Int. 2021. PMID: 33980088
References
-
- Regnerus M, Smith CA, Fritsch M. Religion in the lives of American adolescents: a review of the literature. Chapel Hill: National study of youth and religion; 2003.
-
- WHO. Adolescent health – the missing population in universal health coverage. World Health Organization; 2016.
-
- WHO. Recognizing adolescence. 2014. Retrieved on 01/07/22 from http://www.who.int/about/copyright/en/.
-
- Schwadel P, Hardy SA. What aspects of religiosity are associated with values? J Sci Study Relig. 2022;61(2):374–88. doi: 10.1111/jssr.12777. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

