This is a preprint.
An encyclopedia of enhancer-gene regulatory interactions in the human genome
- PMID: 38014075
- PMCID: PMC10680627
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.09.563812
An encyclopedia of enhancer-gene regulatory interactions in the human genome
Abstract
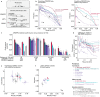
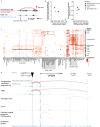
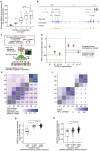
Identifying transcriptional enhancers and their target genes is essential for understanding gene regulation and the impact of human genetic variation on disease1-6. Here we create and evaluate a resource of >13 million enhancer-gene regulatory interactions across 352 cell types and tissues, by integrating predictive models, measurements of chromatin state and 3D contacts, and largescale genetic perturbations generated by the ENCODE Consortium7. We first create a systematic benchmarking pipeline to compare predictive models, assembling a dataset of 10,411 elementgene pairs measured in CRISPR perturbation experiments, >30,000 fine-mapped eQTLs, and 569 fine-mapped GWAS variants linked to a likely causal gene. Using this framework, we develop a new predictive model, ENCODE-rE2G, that achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple prediction tasks, demonstrating a strategy involving iterative perturbations and supervised machine learning to build increasingly accurate predictive models of enhancer regulation. Using the ENCODE-rE2G model, we build an encyclopedia of enhancer-gene regulatory interactions in the human genome, which reveals global properties of enhancer networks, identifies differences in the functions of genes that have more or less complex regulatory landscapes, and improves analyses to link noncoding variants to target genes and cell types for common, complex diseases. By interpreting the model, we find evidence that, beyond enhancer activity and 3D enhancer-promoter contacts, additional features guide enhancerpromoter communication including promoter class and enhancer-enhancer synergy. Altogether, these genome-wide maps of enhancer-gene regulatory interactions, benchmarking software, predictive models, and insights about enhancer function provide a valuable resource for future studies of gene regulation and human genetics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement Z.A. is employed by Google DeepMind. J.C.U. is an employee of Illumina, Inc. D.R.K. is employed by Calico Life Sciences LLC. Z.W. co-founded Rgenta Therapeutics, and she serves as a scientific advisor for the company and is a member of its board. W.J.G. is an inventor on IP licensed by 10x Genomics. A.Kundaje is on the scientific advisory board of PatchBio, SerImmune and OpenTargets, was a consultant with Illumina, and owns shares in DeepGenomics, ImmunAI and Freenome. J.M.E. is a consultant and equity holder in Martingale Labs, Inc. and has received materials from 10x Genomics unrelated to this study.
Figures



References
-
- Zaugg J. B. et al. Current challenges in understanding the role of enhancers in disease. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 29, 1148–1158 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- U24 HG009397/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HG012203/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009431/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HG011324/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG012103/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG011972/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG012069/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000044/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HG009917/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009380/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009395/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HG009917/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG012009/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG012367/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG006992/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG009436/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG009446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
