This is a preprint.
A Multi-task Platform for Profiling Cognitive and Motivational Constructs in Humans and Nonhuman Primates
- PMID: 38014107
- PMCID: PMC10680597
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.09.566422
A Multi-task Platform for Profiling Cognitive and Motivational Constructs in Humans and Nonhuman Primates
Abstract
Background: Understanding the neurobiological substrates of psychiatric disorders requires comprehensive evaluations of cognitive and motivational functions in preclinical research settings. The translational validity of such evaluations will be supported by (1) tasks with high construct validity that are engaging and easy to teach to human and nonhuman participants, (2) software that enables efficient switching between multiple tasks in single sessions, (3) software that supports tasks across a broad range of physical experimental setups, and (4) by platform architectures that are easily extendable and customizable to encourage future optimization and development.
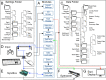
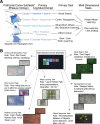
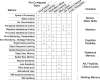
New method: We describe the Multi-task Universal Suite for Experiments (M-USE), a software platform designed to meet these requirements. It leverages the Unity video game engine and C# programming language to (1) support immersive and engaging tasks for humans and nonhuman primates, (2) allow experimenters or participants to switch between multiple tasks within-session, (3) generate builds that function across computers, tablets, and websites, and (4) is freely available online with documentation and tutorials for users and developers. M-USE includes a task library with seven pre-existing tasks assessing cognitive and motivational constructs of perception, attention, working memory, cognitive flexibility, motivational and affective self-control, relational long-term memory, and visuo-spatial problem solving.
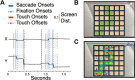
Results: M-USE was used to test NHPs on up to six tasks per session, all available as part of the Task Library, and to extract performance metrics for all major cognitive and motivational constructs spanning the Research Domain Criteria (RDoC) of the National Institutes of Mental Health.
Comparison with existing methods: Other experiment design and control systems exist, but do not provide the full range of features available in M-USE, including a pre-existing task library for cross-species assessments; the ability to switch seamlessly between tasks in individual sessions; cross-platform build capabilities; license-free availability; and its leveraging of video-engine capabilities used to gamify tasks.
Conclusions: The new multi-task platform facilitates cross-species translational research for understanding the neurobiological substrates of higher cognitive and motivational functions.
Keywords: Diagnostic Battery; naturalistic behavior; nonhuman primates; video-engine; virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial Disclosures The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Aragona M. (2014). Epistemological reflections about the crisis of the DSM-5 and the revolutionary potential of the RDoC project. Dialogues in Philosophy, Mental and Neuro Sciences, 7(1), 11–20.
-
- Axelsson S. F. A., Horst N. K., Horiguchi N., Roberts C., A., & Robbins T. W. (2021). Flexible versus Fixed Spatial Self-Ordered Response Sequencing: Effects of Inactivation and Neurochemical Modulation of Ventrolateral Prefrontal Cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 41(34), 7246–7258. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0227-21.2021 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
