This is a preprint.
Targeted brain-specific tauopathy compromises peripheral skeletal muscle integrity and function
- PMID: 38014109
- PMCID: PMC10680826
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.17.567586
Targeted brain-specific tauopathy compromises peripheral skeletal muscle integrity and function
Update in
-
Targeted brain-specific tauopathy compromises peripheral skeletal muscle integrity and function.Aging Brain. 2024 Feb 24;5:100110. doi: 10.1016/j.nbas.2024.100110. eCollection 2024. Aging Brain. 2024. PMID: 38419621 Free PMC article.
Abstract
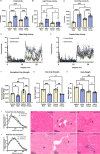
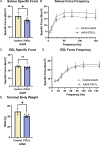
Tauopathies are neurodegenerative disorders in which the pathological intracellular aggregation of the protein tau causes cognitive deficits. Additionally, clinical studies report muscle weakness in populations with tauopathy. However, whether neuronal pathological tau species confer muscle weakness, and whether skeletal muscle maintains contractile capacity in primary tauopathy remains unknown. Here, we identified skeletal muscle abnormalities in a mouse model of primary tauopathy, expressing human mutant P301L-tau using adeno-associated virus serotype 8 (AAV8). AAV8-P301L mice showed grip strength deficits, hyperactivity, and abnormal histological features of skeletal muscle. Additionally, spatially resolved gene expression of muscle cross sections were altered in AAV8-P301L myofibers. Transcriptional changes showed alterations of genes encoding sarcomeric proteins, proposing a weakness phenotype. Strikingly, specific force of the soleus muscle was blunted in AAV8-P301L tau male mice. Our findings suggest tauopathy has peripheral consequences in skeletal muscle that contribute to weakness in tauopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
