This is a preprint.
Single cell spatial transcriptomic profiling of childhood-onset lupus nephritis reveals complex interactions between kidney stroma and infiltrating immune cells
- PMID: 38014158
- PMCID: PMC10680641
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.09.566503
Single cell spatial transcriptomic profiling of childhood-onset lupus nephritis reveals complex interactions between kidney stroma and infiltrating immune cells
Update in
-
Childhood-onset lupus nephritis is characterized by complex interactions between kidney stroma and infiltrating immune cells.Sci Transl Med. 2024 Nov 27;16(775):eadl1666. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adl1666. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Sci Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39602512 Free PMC article.
Abstract
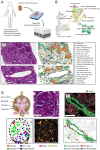
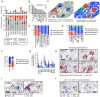
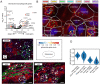
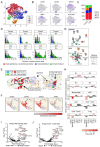
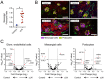
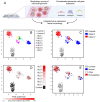
Children with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are at increased risk of developing kidney disease, termed childhood-onset lupus nephritis (cLN). Single cell transcriptomics of dissociated kidney tissue has advanced our understanding of LN pathogenesis, but loss of spatial resolution prevents interrogation of in situ cellular interactions. Using a technical advance in spatial transcriptomics, we generated a spatially resolved, single cell resolution atlas of kidney tissue (>400,000 cells) from eight cLN patients and two controls. Annotated cells were assigned to 35 reference cell types, including major kidney subsets and infiltrating immune cells. Analysis of spatial distribution demonstrated that individual immune lineages localize to specific regions in cLN kidneys, including myeloid cells trafficking to inflamed glomeruli and B cells clustering within tubulointerstitial immune hotspots. Notably, gene expression varied as a function of tissue location, demonstrating how incorporation of spatial data can provide new insights into the immunopathogenesis of SLE. Alterations in immune phenotypes were accompanied by parallel changes in gene expression by resident kidney stromal cells. However, there was little correlation between histologic scoring of cLN disease activity and glomerular cell transcriptional signatures at the level of individual glomeruli. Finally, we identified modules of spatially-correlated gene expression with predicted roles in induction of inflammation and the development of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. In summary, single cell spatial transcriptomics allows unprecedented insights into the molecular heterogeneity of cLN, paving the way towards more targeted and personalized treatment approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests. P.D. is an employee and shareholder of NanoString Technologies, Inc. and has filed a provisional patent covering the algorithm for spatial correlation analyses described in this manuscript. N.H. no disclosures. E.D.N: no disclosures. K.H. received an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer Global medical grants to support a quality improvement program for patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) which was unrelated to the current study. N.R.: no disclosures. C.E.A.: no disclosures. R.C.R: no disclosures. D.M.O. is a consultant for a Horizon Therapeutics Advisory Board. S.K.B. is an employee and shareholder of Sanofi. S.W.J. is a consultant for Bristol-Myers Squib and previously served as a consultant for Variant Bio and ChemoCentryx, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Furie R., Rovin B. H., Houssiau F., Malvar A., Teng Y. K. O., Contreras G., Amoura Z., Yu X., Mok C. C., Santiago M. B., Saxena A., Green Y., Ji B., Kleoudis C., Burriss S. W., Barnett C., Roth D. A., Two-Year, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Belimumab in Lupus Nephritis. N Engl J Med 383, 1117–1128 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Rovin B. H., Solomons N., Pendergraft W. F. 3rd, Dooley M. A., Tumlin J., Romero-Diaz J., Lysenko L., Navarra S. V., Huizinga R. B., Group A.-L. S., A randomized, controlled double-blind study comparing the efficacy and safety of dose-ranging voclosporin with placebo in achieving remission in patients with active lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 95, 219–231 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Rovin B. H., Teng Y. K. O., Ginzler E. M., Arriens C., Caster D. J., Romero-Diaz J., Gibson K., Kaplan J., Lisk L., Navarra S., Parikh S. V., Randhawa S., Solomons N., Huizinga R. B., Efficacy and safety of voclosporin versus placebo for lupus nephritis (AURORA 1): a double-blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 397, 2070–2080 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Arazi A., Rao D. A., Berthier C. C., Davidson A., Liu Y., Hoover P. J., Chicoine A., Eisenhaure T. M., Jonsson A. H., Li S., Lieb D. J., Zhang F., Slowikowski K., Browne E. P., Noma A., Sutherby D., Steelman S., Smilek D. E., Tosta P., Apruzzese W., Massarotti E., Dall’Era M., Park M., Kamen D. L., Furie R. A., Payan-Schober F., Pendergraft W. F. 3rd, McInnis E. A., Buyon J. P., Petri M. A., Putterman C., Kalunian K. C., Woodle E. S., Lederer J. A., Hildeman D. A., Nusbaum C., Raychaudhuri S., Kretzler M., Anolik J. H., Brenner M. B., Wofsy D., Hacohen N., Diamond B., n. S. L. E. Accelerating Medicines Partnership in, The immune cell landscape in kidneys of patients with lupus nephritis. Nat Immunol 20, 902–914 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
