This is a preprint.
JUN mRNA Translation Regulation is Mediated by Multiple 5' UTR and Start Codon Features
- PMID: 38014201
- PMCID: PMC10680820
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.17.567602
JUN mRNA Translation Regulation is Mediated by Multiple 5' UTR and Start Codon Features
Update in
-
JUN mRNA translation regulation is mediated by multiple 5' UTR and start codon features.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 14;19(3):e0299779. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299779. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38483896 Free PMC article.
Abstract
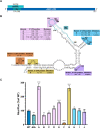
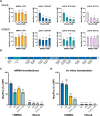
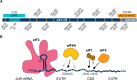
Regulation of mRNA translation by eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) is crucial for cell survival. In humans, eIF3 stimulates translation of the JUN mRNA which encodes the transcription factor JUN, an oncogenic transcription factor involved in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and cell proliferation. Previous studies revealed that eIF3 activates translation of the JUN mRNA by interacting with a stem loop in the 5' untranslated region (5' UTR) and with the 5'-7-methylguanosine cap structure. In addition to its interaction site with eIF3, the JUN 5' UTR is nearly one kilobase in length, and has a high degree of secondary structure, high GC content, and an upstream start codon (uAUG). This motivated us to explore the complexity of JUN mRNA translation regulation in human cells. Here we find that JUN translation is regulated in a sequence and structure-dependent manner in regions adjacent to the eIF3-interacting site in the JUN 5' UTR. Furthermore, we identify contributions of an additional initiation factor, eIF4A, in JUN regulation. We show that enhancing the interaction of eIF4A with JUN by using the compound Rocaglamide A (RocA) represses JUN translation. We also find that both the upstream AUG (uAUG) and the main AUG (mAUG) contribute to JUN translation and that they are conserved throughout vertebrates. Our results reveal additional layers of regulation for JUN translation and show the potential of JUN as a model transcript for understanding multiple interacting modes of translation regulation.
Keywords: 5′ untranslated region; JUN mRNA; eukaryotic initiation factors; start codon; translation initiation.
Figures

References
-
- Aitken CE, Lorsch JR. 2012. A mechanistic overview of translation initiation in eukaryotes. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19: 568–576. - PubMed
-
- Aleksashin N, Chang ST-L, Cate J. 2023. A highly efficient human cell-free translation system. RNA rna.079825.123. http://rnajournal.cshlp.org/content/early/2023/10/04/rna.079825.123. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angel P, Hattori K, Smeal T, Karin M. 1988. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell 55: 875–885. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
