This is a preprint.
Microglia Depletion Reduces Human Neuronal APOE4-Driven Pathologies in a Chimeric Alzheimer's Disease Model
- PMID: 38014339
- PMCID: PMC10680610
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.10.566510
Microglia Depletion Reduces Human Neuronal APOE4-Driven Pathologies in a Chimeric Alzheimer's Disease Model
Update in
-
Microglia depletion reduces human neuronal APOE4-related pathologies in a chimeric Alzheimer's disease model.Cell Stem Cell. 2025 Jan 2;32(1):86-104.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2024.10.005. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Cell Stem Cell. 2025. PMID: 39500314 Free PMC article.
Abstract
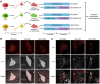
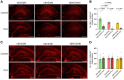
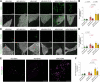
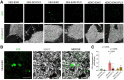
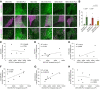
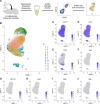
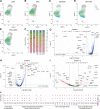
Despite strong evidence supporting the involvement of both apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4) and microglia in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) pathogenesis, the effects of microglia on neuronal APOE4-driven AD pathogenesis remain elusive. Here, we examined such effects utilizing microglial depletion in a chimeric model with human neurons in mouse hippocampus. Specifically, we transplanted homozygous APOE4, isogenic APOE3, and APOE-knockout (APOE-KO) induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived human neurons into the hippocampus of human APOE3 or APOE4 knock-in mice, and depleted microglia in half the chimeric mice. We found that both neuronal APOE and microglial presence were important for the formation of Aβ and tau pathologies in an APOE isoform-dependent manner (APOE4 > APOE3). Single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis identified two pro-inflammatory microglial subtypes with high MHC-II gene expression that are enriched in chimeric mice with human APOE4 neuron transplants. These findings highlight the concerted roles of neuronal APOE, especially APOE4, and microglia in AD pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests Y.Huang is a cofounder and scientific advisory board member of GABAeron, Inc. Other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Corder E. H. et al. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261, 921–923 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Corder E. H. et al. Protective effect of apolipoprotein E type 2 allele for late onset Alzheimer disease. Nat. Genet. 7, 180–184 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Koutsodendris N., Nelson M. R., Rao A. & Huang Y. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s Disease: Findings, Hypotheses, and Potential Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 17, 73–99 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
