This is a preprint.
Virus specificity and nucleoporin requirements for MX2 activity are affected by GTPase function and capsid-CypA interactions
- PMID: 38014352
- PMCID: PMC10680775
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.16.567336
Virus specificity and nucleoporin requirements for MX2 activity are affected by GTPase function and capsid-CypA interactions
Update in
-
Virus specificity and nucleoporin requirements for MX2 activity are affected by GTPase function and capsid-CypA interactions.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Mar 21;20(3):e1011830. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011830. eCollection 2024 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38512975 Free PMC article.
Abstract
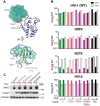
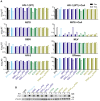
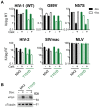
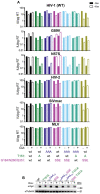
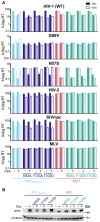
Human myxovirus resistance 2 (MX2/MXB) is an interferon-induced GTPase that inhibits human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) infection by preventing nuclear import of the viral preintegration complex. The HIV-1 capsid (CA) is the major viral determinant for sensitivity to MX2, and complex interactions between MX2, CA, nucleoporins (Nups), cyclophilin A (CypA), and other cellular proteins influence the outcome of viral infection. To explore the interactions between MX2, the viral CA, and CypA, we utilized a CRISPR-Cas9/AAV approach to generate CypA knock-out cell lines as well as cells that express CypA from its endogenous locus, but with specific point mutations that would abrogate CA binding but should not affect enzymatic activity or cellular function. We found that infection of CypA knock-out and point mutant cell lines with wild-type HIV-1 and CA mutants recapitulated the phenotypes observed upon cyclosporine A (CsA) addition, indicating that effects of CsA treatment are the direct result of blocking CA-CypA interactions and are therefore independent from potential interactions between CypA and MX2 or other cellular proteins. Notably, abrogation of GTP hydrolysis by MX2 conferred enhanced antiviral activity when CA-CypA interactions were abolished, and this effect was not mediated by the CA-binding residues in the GTPase domain, or by phosphorylation of MX2 at position T151. We additionally found that elimination of GTPase activity also altered the Nup requirements for MX2 activity. Our data demonstrate that the antiviral activity of MX2 is affected by CypA-CA interactions in a virus-specific and GTPase activity-dependent manner. These findings further highlight the importance of the GTPase domain of MX2 in regulation of substrate specificity and interaction with nucleocytoplasmic trafficking pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Stetson DB, Medzhitov R. Type I interferons in host defense. Immunity. 2006;25(3):373–81. - PubMed
-
- Haller O, Staeheli P, Schwemmle M, Kochs G. Mx GTPases: dynamin-like antiviral machines of innate immunity. Trends in microbiology. 2015;23(3):154–63. - PubMed
-
- Melen K, Keskinen P, Ronni T, Sareneva T, Lounatmaa K, Julkunen I. Human MxB protein, an interferon-alpha-inducible GTPase, contains a nuclear targeting signal and is localized in the heterochromatin region beneath the nuclear envelope. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1996;271(38):23478–86. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
