Biophysical Interaction Landscape of Mycobacterial Mycolic Acids and Phenolic Glycolipids with Host Macrophage Membranes
- PMID: 38015441
- PMCID: PMC7617140
- DOI: 10.1021/acsabm.3c00748
Biophysical Interaction Landscape of Mycobacterial Mycolic Acids and Phenolic Glycolipids with Host Macrophage Membranes
Abstract
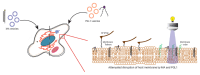
Lipidic adjuvant formulations consisting of immunomodulatory mycobacterial cell wall lipids interact with host cells following administration. The impact of this cross-talk on the host membrane's structure and function is rarely given enough consideration but is imperative to rule out nonspecific perturbation underlying the adjuvant. In this work, we investigated changes in the plasma membranes of live mammalian cells after exposure to mycobacterial mycolic acid (MA) and phenolic glycolipids, two strong candidates for lipidic adjuvant therapy. We found that phenolic glycolipid 1 softened the plasma membrane, lowering membrane tension and stiffness, but MA did not significantly change the membrane characteristics. Further, phenolic glycolipid 1 had a fluidizing impact on the host plasma membrane, increasing the fluidity and the abundance of fluid-ordered-disordered coexisting lipid domains. Notably, lipid diffusion was not impacted. Overall, MA and, to a lesser extent, phenolic glycolipid 1, due to minor disruption of host cell membranes, may serve as appropriate lipids in adjuvant formulations.
Keywords: fluidity; infectious diseases; lateral membrane organization; mycobacterial lipids; plasma membrane; vaccine adjuvants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Minnikin DE. In: The Biology of Mycobacteria. Ratledge C, Stanford J, editors. Vol. 1. Academic Press; London: 1982. Lipids: Complex lipids, their chemistry, biosynthesis and roles; pp. 95–184.
-
- Sprott GD, Dicaire CJ, Gurnani K, Sad S, Krishnan L. Activation of Dendritic Cells by Liposomes Prepared from Phosphatidylinositol Mannosides from Mycobacterium Bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guérin and Adjuvant Activity in Vivo. Infect Immun. 2004;72(9):5235–5246. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5235-5246.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersen CAS, Rosenkrands I, Olsen AW, Nordly P, Christensen D, Lang R, Kirschning C, Gomes JM, Bhowruth V, Minnikin DE, Besra GS, et al. Novel Generation Mycobacterial Adjuvant Based on Liposome-Encapsulated Monomycoloyl Glycerol from Mycobacterium Bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin. J Immunol. 2009;183(4):2294–2302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
