Altered profiles of circulating cytokines in chronic liver diseases (NAFLD/HCC): Impact of the PNPLA3I148M risk allele
- PMID: 38015590
- PMCID: PMC10667005
- DOI: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000306
Altered profiles of circulating cytokines in chronic liver diseases (NAFLD/HCC): Impact of the PNPLA3I148M risk allele
Abstract
Background: Individuals carrying the risk variant p.I148M of patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 (PNPLA3) have a higher susceptibility to fatty liver diseases and associated complications, including HCC, a cancer closely linked to chronic inflammation. Here, we assessed circulating cytokine profiles for patients with chronic liver diseases genotyped for PNPLA3.
Methods: Serum concentrations of 22 cytokines were measured by multiplex sandwich-ELISA. The cohort comprised 123 individuals: 67 patients with NAFLD without cirrhosis (57 steatosis, 10 NASH), 24 patients with NAFLD with cirrhosis, 21 patients with HCC (15 cirrhosis), and 11 healthy controls. Receiver operator characteristic analyses were performed to assess the suitability of the cytokine profiles for the prediction of steatosis, cirrhosis, and HCC.
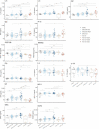
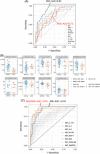
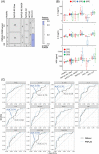
Results: HGF, IL-6, and IL-8 levels were increased in patients, with ∼2-fold higher levels in patients with cirrhosis versus healthy, while platelet derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) and regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted (RANTES) showed lower concentrations compared to controls. Migration inhibitory factor and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) were found at higher levels in NAFLD samples (maximum: NAFLD-cirrhosis) versus healthy controls and HCC samples. In receiver operator characteristic analyses, migration inhibitory factor, IL-8, IL-6, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 yielded high sensitivity scores for predicting noncirrhotic NAFLD (vs. healthy). The top combination to predict cirrhosis was HGF plus PDGF-BB. Migration inhibitory factor performed best to discriminate HCC from NAFLD; the addition of monokine induced gamma (MIG), RANTES, IL-4, macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), or IL-17A as second parameters further increased the AUC values (> 0.9). No significant impact of the PNPLA3I148M allele on cytokine levels was observed in this cohort.
Conclusions: Cytokines have biomarker potential in patients with fatty liver, possibly suited for early HCC detection in patients with fatty liver. Patients carrying the PNPLA3 risk allele did not present significantly different levels of circulating cytokines.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to report.
Figures



References
-
- Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:6. - PubMed
-
- Riazi K, Azhari H, Charette JH, Underwood FE, King JA, Afshar EE, et al. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7:851–861. - PubMed
-
- Krawczyk M, Liebe R, Lammert F. Toward Genetic Prediction of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Trajectories: PNPLA3 and Beyond. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1865–1880.e1861. - PubMed
-
- Cherubini A, Casirati E, Tomasi M, Valenti L. PNPLA3 as a therapeutic target for fatty liver disease: The evidence to date. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2021;25:1033–1043. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

