Segmentation of lung lobes and lesions in chest CT for the classification of COVID-19 severity
- PMID: 38017029
- PMCID: PMC10684885
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-47743-z
Segmentation of lung lobes and lesions in chest CT for the classification of COVID-19 severity
Abstract
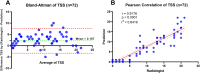
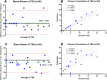
To precisely determine the severity of COVID-19-related pneumonia, computed tomography (CT) is an imaging modality beneficial for patient monitoring and therapy planning. Thus, we aimed to develop a deep learning-based image segmentation model to automatically assess lung lesions related to COVID-19 infection and calculate the total severity score (TSS). The entire dataset consisted of 124 COVID-19 patients acquired from Chulabhorn Hospital, divided into 28 cases without lung lesions and 96 cases with lung lesions categorized severity by radiologists regarding TSS. The model used a 3D-UNet along with DenseNet and ResNet models that had already been trained to separate the lobes of the lungs and figure out the percentage of lung involvement due to COVID-19 infection. It also used the Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) to measure TSS. Our final model, consisting of 3D-UNet integrated with DenseNet169, achieved segmentation of lung lobes and lesions with the Dice similarity coefficients of 91.52% and 76.89%, respectively. The calculated TSS values were similar to those evaluated by radiologists, with an R2 of 0.842. The correlation between the ground-truth TSS and model prediction was greater than that of the radiologist, which was 0.890 and 0.709, respectively.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Abnormal lung quantification in chest CT images of COVID-19 patients with deep learning and its application to severity prediction.Med Phys. 2021 Apr;48(4):1633-1645. doi: 10.1002/mp.14609. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33225476 Free PMC article.
-
A deep learning-based application for COVID-19 diagnosis on CT: The Imaging COVID-19 AI initiative.PLoS One. 2023 May 2;18(5):e0285121. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285121. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37130128 Free PMC article.
-
Two-stage hybrid network for segmentation of COVID-19 pneumonia lesions in CT images: a multicenter study.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022 Sep;60(9):2721-2736. doi: 10.1007/s11517-022-02619-8. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022. PMID: 35856130 Free PMC article.
-
Automated Detection and Quantification of COVID-19 Airspace Disease on Chest Radiographs: A Novel Approach Achieving Expert Radiologist-Level Performance Using a Deep Convolutional Neural Network Trained on Digital Reconstructed Radiographs From Computed Tomography-Derived Ground Truth.Invest Radiol. 2021 Aug 1;56(8):471-479. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000763. Invest Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33481459
-
From community-acquired pneumonia to COVID-19: a deep learning-based method for quantitative analysis of COVID-19 on thick-section CT scans.Eur Radiol. 2020 Dec;30(12):6828-6837. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07042-x. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32683550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ACR recommendations for the use of chest radiography and computed tomography (CT) for suspected COVID-19 infection. Acr.org https://www.acr.org/Advocacy-and-Economics/ACR-Position-Statements/Recom... (2020).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

