Neuroprotective Effects of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy
- PMID: 38018498
- PMCID: PMC10687918
- DOI: 10.1177/09636897231213309
Neuroprotective Effects of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy
Abstract
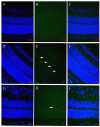
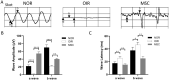
This study was designed to provide evidence of the neuroprotective of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hADSCs) in oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR). In vivo, hADSCs were intravitreally injected into OIR mice. Various assessments, including HE (histological evaluation), TUNEL (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling) staining, electroretinogram (ERG) analysis, and retinal flat-mount examination, were performed separately at postnatal days 15 (P15) and 17 (P17) to evaluate neurological damage and functional changes. Western blot analysis of ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) was conducted at P17 to elucidate the neuroprotective mechanism. The P17 OIR group exhibited a significant increase in vascular endothelial cell nuclei and neovascularization that breached the ILM (inner limiting membrane) to the P17 control group. In addition, the retinal nonperfusion areas in the P17 OIR group and the number of apoptotic retinal cells in the P15 OIR group were significantly higher than in the corresponding hADSCs treatment group and control group. There was no significant thickness change in the inner nuclear layer (INL) but the outer nuclear layer (ONL) in the P17 OIR treatment group compared with the P17 OIR group. The cell density in the INL and ONL at P17 in the hADSCs treatment group was not significantly different from the OIR group. The amplitude of a-wave and b-wave in scotopic ERG analysis for the P17 OIR group was significantly lower than in the P17 hADSCs treatment group and the P17 control group. Furthermore, the latency of the a-wave and b-wave in the P17 OIR group was significantly longer than in the P17 hADSCs treatment group and the P17 control group. In addition, the expression levels of CNTF and BDNF in the P17 OIR group were statistically higher than those in the P17 control group, whereas the expression of GDNF was statistically lower in the P17 OIR group, compared with the P17 control group. The expression of CNTF and GDNF in the P17 hADSCs treatment group was statistically higher than in the P17 OIR group. However, the expression of BDNF in the P17 hADSCs treatment group was statistically lower than in the P17 OIR group. This study provides evidence for the neuroprotective effects of hADSCs in OIR.
Keywords: TUNEL; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; ciliary neurotrophic factor; electroretinogram; glial cell line–derived neurotrophic factor; histological evaluation; human adipose–derived mesenchymal stem cells; neuroprotection; oxygen-induced retinopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of the neuroprotective factors BDNF, CNTF, and FGF-2 in normal and oxygen induced retinopathy.Front Neurosci. 2022 Dec 2;16:971952. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.971952. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36532277 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells provide paracrine neuroprotective resources that delay degeneration of co-cultured organotypic neuroretinal cultures.Exp Eye Res. 2019 Aug;185:107671. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2019.05.011. Epub 2019 May 17. Exp Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 31108056
-
CNTF Attenuates Vasoproliferative Changes Through Upregulation of SOCS3 in a Mouse-Model of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Aug 1;57(10):4017-26. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-18508. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27494343 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro induction and intraocular application in oxygen-induced retinopathy of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Mol Vis. 2022 Dec 21;28:432-440. eCollection 2022. Mol Vis. 2022. PMID: 36601410 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting neurotrophic dysregulation in diabetic retinopathy: a novel therapeutic avenue.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jun 9;52(1):570. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10671-4. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40488922 Review.
Cited by
-
YTHDC1 Mitigates Apoptosis in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Inhibiting NfƙBiα and Augmenting Cardiac Function Following Myocardial Infarction.Cell Transplant. 2024 Jan-Dec;33:9636897241290910. doi: 10.1177/09636897241290910. Cell Transplant. 2024. PMID: 39466658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osborne NN, Casson RJ, Wood JP, Chidlow G, Graham M, Melena J. Retinal ischemia: mechanisms of damage and potential therapeutic strategies. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004;23(1):91–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

