Designing phage cocktails to combat the emergence of bacteriophage-resistant mutants in multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 38018985
- PMCID: PMC10783003
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01258-23
Designing phage cocktails to combat the emergence of bacteriophage-resistant mutants in multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
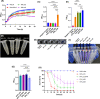
In this study, we aimed to design a novel and effective bacteriophage cocktail that can target both wild-type bacteria and phage-resistant mutants. To achieve this goal, we isolated four phages (U2874, phi_KPN_H2, phi_KPN_S3, and phi_KPN_HS3) that recognized different bacterial surface molecules using phage-resistant bacteria. We constructed three phage cocktails and tested their phage resistance-suppressing ability against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. We argue that the phage cocktail that induces resensitization of phage susceptibility exhibited superior phage resistance-suppressing ability. Moreover, we observed trade-off effects that manifested progressively in phage-resistant bacteria. We hypothesize that such trade-off effects can augment therapeutic efficacy. We also recommend collating phage host range data against phage-resistant mutants in addition to wild-type bacteria when establishing phage banks to improve the efficiency of phage therapy. Our study underscores the importance of phage host range data in constructing effective phage cocktails for clinical use.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; bacteriophage; phage cocktail; phage resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Targeted phage hunting to specific Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates is an efficient antibiotic resistance and infection control strategy.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 3;12(10):e0025424. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00254-24. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39194291 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophage-antibiotic synergy enhances therapeutic efficacy against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections.J Appl Microbiol. 2025 Jun 2;136(6):lxaf131. doi: 10.1093/jambio/lxaf131. J Appl Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40440204
-
Fitness Trade-Offs in Phage Cocktail-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Results in Increased Antibiotic Susceptibility and Reduced Virulence.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0291422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02914-22. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36165776 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophages as a potential substitute for antibiotics: A comprehensive review.Cell Biochem Funct. 2024 Apr;42(3):e4022. doi: 10.1002/cbf.4022. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024. PMID: 38655589 Review.
-
Bacteriophage therapy for inhibition of multi drug-resistant uropathogenic bacteria: a narrative review.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021 Apr 26;20(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12941-021-00433-y. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021. PMID: 33902597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Studies in vitro and in vivo of phage therapy medical products (PTMPs) Targeting Clinical Strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae belonging to the clone ST512.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Jun 4;69(6):e0193524. doi: 10.1128/aac.01935-24. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 40265927 Free PMC article.
-
The potential use of bacteriophages as antibacterial agents against Klebsiella pneumoniae.Virol J. 2024 Aug 19;21(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02450-7. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 39160541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro and in vivo selection and cost of bacteriophage resistance on natural Escherichia coli.Microlife. 2025 Aug 11;6:uqaf017. doi: 10.1093/femsml/uqaf017. eCollection 2025. Microlife. 2025. PMID: 40837842 Free PMC article.
-
High activity and specificity of bacteriophage cocktails against carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae belonging to the high-risk clones CG258 and ST307.Front Microbiol. 2024 Dec 9;15:1502593. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1502593. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39717270 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Treatment of a Patient With Chronic Bronchiectasis Using an Induced Native Phage Cocktail: A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 Jan 19;17(1):e77681. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77681. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39834667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osei KM, Choi H-K, Zeyeh DE, Alikamatu S, Boateng EO, Nov V, Nguyen LP, Kubura K, Bobzah B, Yong D-E. 2022. Multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections in a tertiary-care hospital in northern Ghana: a three-year retrospective analysis. Ann Clin Microbiol 25:1–11. doi:10.5145/ACM.2022.25.1.1 - DOI
-
- Kim YA, Jeong SH, Shin JH, Shin KS, Shin JH, Kim YR, Kim HS, Uh Y, Ryoo NH. 2021. Antimicrobial resistance patterns of Acinetobacter Baumannii and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa isolated from vulnerable patients in Korea, 2021. Annals of Clinical Microbiology 25:145–153. doi:10.5145/ACM.2022.25.4.4 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

