Genetic Polymorphism in Xenobiotic Metabolising Genes and Increased Oxidative Stress among Pesticides Exposed Agricultural Workers Diagnosed with Cancers
- PMID: 38019237
- PMCID: PMC10772756
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.11.3795
Genetic Polymorphism in Xenobiotic Metabolising Genes and Increased Oxidative Stress among Pesticides Exposed Agricultural Workers Diagnosed with Cancers
Abstract
Background: Oxidative stress combined with nullity of xenobiotic metabolizing GSTT1/GSTM1/CYP2E1 genes may increase the susceptibility of agricultural workers to adverse health effects including cancer. The present study was conducted to determine; the prevalence of polymorphisms in GSTM1, GSTT1 and CYP2E1 genes, serum 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxygunosine levels, and the role of these markers in risk of cancer among agricultural workers occupationally exposed to pesticides.
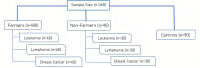
Methods: A total of 360 participants, of which 180 belonging to farming group diagnosed with leukemia (n=60), lymphoma (n=60) and breast cancers (n=60), 90 in non-farming group diagnosed with similar cancers and the other 90 as healthy controls with neither history of occupational exposure nor diagnosed with any type of cancers were recruited. Following the questionnaire survey, serum 8-OHdG and genetic polymorphisms in the three genes were determined using ELISA and PCR methods respectively.
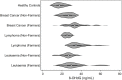
Results: The results of the study revealed that farm workers carrying GSTT1 null genotype had increased risk for lymphoma (OR = 5.34; 95% CI = 1.80-15.82) and breast cancer (OR=4.04; 95% CI = 1.24-13.07). For farm workers carrying GSTM1 null genotype, the risk was six-fold for breast cancer (OR = 6.88; 95% CI =1.88-25.99). Further, there found a significant difference between 8-OHdG and nullity of CYP2E1 among the farm workers diagnosed with leukemia.
Conclusion: The findings of the present study suggest that the polymorphisms in detoxifying genes among farm workers occupationally exposed to pesticides and the oxidative stress may likely be responsible for triggering the mechanism of malignancy.
Keywords: Genetic polymorphism; OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE; Pesticides; cancer; oxidative stress.
Figures
References
-
- Agúndez JA, Ladero JM. Glutathione S-transferase GSTT1 and GSTM1 allozymes: beyond null alleles. Pharmacogenomics. 2008;9:359–63. - PubMed
-
- Ahluwalia M, Kaur A. Modulatory role of GSTT1 and GSTM1 in Punjabi agricultural workers exposed to pesticides. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2018;25:11981–6. - PubMed
-
- Andreoli C, Gregg EO, Puntoni R, et al. Cross-sectional study of biomarkers of exposure and biological effect on monozygotic twins discordant for smoking. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011;49:137–45. - PubMed
-
- Aydin‐Sayitoglu M, Hatirnaz O, Erensoy N, Ozbek U. Role of CYP2D6, CYP1A1, CYP2E1, GSTT1, and GSTM1 genes in the susceptibility to acute leukemias. Am J Hematol. 2006;81:162–70. - PubMed
-
- Bin Q, Luo J. Role of polymorphisms of GSTM1, GSTT1 and GSTP1 Ile105Val in Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma risk: a Human Genome Epidemiology (HuGE) review. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013;54:14–20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous