Toxicity of Carboplatin-Niosomal Nanoparticles in a Brain Cancer Cell Line
- PMID: 38019259
- PMCID: PMC10772781
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.11.3985
Toxicity of Carboplatin-Niosomal Nanoparticles in a Brain Cancer Cell Line
Abstract
Objective: Cancer poses a significant challenge in modern medicine, standing as the primary cause of death in many countries, second only to cardiovascular diseases. Among the various treatments available, carboplatin, a chemotherapy drug, is employed for specific cancer types, including brain carcinoma. The main objective of this investigation is to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of carboplatin by utilizing niosomal nanocarriers.
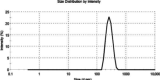
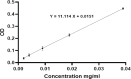
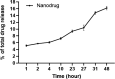
Methods: We synthesized nanoniosomal carboplatin using the reverse-phase evaporation technique and conducted an assessment of its particle size, zeta potential, and drug-release properties. Subsequently, we evaluated the cytotoxicity of nanoniosomal carboplatin using the C6 rat glioma cell line.
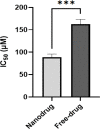
Results: Our research revealed that these niosomal nanoparticles possessed a particle size of 290.5±5.5 nm and a zeta potential of -21.7±7.4 mV. The amount of encapsulated drug and drug loading level were found to be 60.2±2.3% and 2.5±1.1%, respectively. Importantly, the cytotoxic impact of these nanoniosomes on the C6 rat glioma cell line exhibited a significant increase compared to the free drug (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Based on our discoveries, it is evident that carboplatin niosomal nanocarriers hold potential as an innovative approach to chemotherapy for brain cancer therapy.
Keywords: Brain cancer; Carboplatin; Nanoniosome; Nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alavi SE, Raza A, Esfahani MKM, et al. Carboplatin niosomal nanoplatform for potentiated chemotherapy. J Pharm Sci. 2022;111:3029–37. - PubMed
-
- Alimirzaei F, Kieslich CA. Computer Aided Chemical Engineering . Vol. 52. Elsevier; 2023. Machine learning models for predicting membranolytic anticancer peptides; pp. 2691–6.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

