Radiation-induced bone loss in mice is ameliorated by inhibition of HIF-2α in skeletal progenitor cells
- PMID: 38019933
- PMCID: PMC10804914
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abo5217
Radiation-induced bone loss in mice is ameliorated by inhibition of HIF-2α in skeletal progenitor cells
Abstract
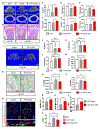
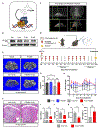
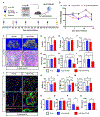
Radiotherapy remains a common treatment modality for cancer despite skeletal complications. However, there are currently no effective treatments for radiation-induced bone loss, and the consequences of radiotherapy on skeletal progenitor cell (SPC) survival and function remain unclear. After radiation, leptin receptor-expressing cells, which include a population of SPCs, become localized to hypoxic regions of the bone and stabilize the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor-2α (HIF-2α), thus suggesting a role for HIF-2α in the skeletal response to radiation. Here, we conditionally knocked out HIF-2α in leptin receptor-expressing cells and their descendants in mice. Radiation therapy in littermate control mice reduced bone mass; however, HIF-2α conditional knockout mice maintained bone mass comparable to nonirradiated control animals. HIF-2α negatively regulated the number of SPCs, bone formation, and bone mineralization. To test whether blocking HIF-2α pharmacologically could reduce bone loss during radiation, we administered a selective HIF-2α inhibitor called PT2399 (a structural analog of which was recently FDA-approved) to wild-type mice before radiation exposure. Pharmacological inhibition of HIF-2α was sufficient to prevent radiation-induced bone loss in a single-limb irradiation mouse model. Given that ~90% of patients who receive a HIF-2α inhibitor develop anemia because of off-target effects, we developed a bone-targeting nanocarrier formulation to deliver the HIF-2α inhibitor to mouse bone, to increase on-target efficacy and reduce off-target toxicities. Nanocarrier-loaded PT2399 prevented radiation-induced bone loss in mice while reducing drug accumulation in the kidney. Targeted inhibition of HIF-2α may represent a therapeutic approach for protecting bone during radiation therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
DGK owns stock and is on the scientific advisory board of Lumicell, which is commercializing intraoperative imaging technology. DGK is a co-founder of Xrad Therapeutics, which is developing radiosensitizers. These interests do not represent a conflict of interest with respect to the design, execution, or interpretation of the studies presented in this manuscript. The DGK laboratory receives research funding from Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Varian Medical Systems, but this funding did not support the research described in this manuscript. CMT is a paid consultant for Xerient Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Barton MB, Jacob S, Shafiq J, Wong K, Thompson SR, Hanna TP, Delaney GP, Estimating the demand for radiotherapy from the evidence: a review of changes from 2003 to 2012. Radiother Oncol 112, 140–144 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Delaney G, Jacob S, Featherstone C, Barton M, The role of radiotherapy in cancer treatment: estimating optimal utilization from a review of evidence-based clinical guidelines. Cancer 104, 1129–1137 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Overgaard M, Spontaneous radiation-induced rib fractures in breast cancer patients treated with postmastectomy irradiation. A clinical radiobiological analysis of the influence of fraction size and dose-response relationships on late bone damage. Acta Oncol 27, 117–122 (1988). - PubMed
-
- Pierce SM, Recht A, Lingos TI, Abner A, Vicini F, Silver B, Herzog A, Harris JR, Long-term radiation complications following conservative surgery (CS) and radiation therapy (RT) in patients with early stage breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 23, 915–923 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Baxter NN, Habermann EB, Tepper JE, Durham SB, Virnig BA, Risk of pelvic fractures in older women following pelvic irradiation. JAMA 294, 2587–2593 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

