Resident microbes shape the vaginal epithelial glycan landscape
- PMID: 38019934
- PMCID: PMC11419735
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abp9599
Resident microbes shape the vaginal epithelial glycan landscape
Abstract
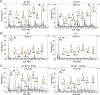
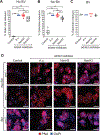
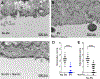
Epithelial cells are covered in carbohydrates (glycans). This glycan coat or "glycocalyx" interfaces directly with microbes, providing a protective barrier against potential pathogens. Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a condition associated with adverse health outcomes in which bacteria reside in direct proximity to the vaginal epithelium. Some of these bacteria, including Gardnerella, produce glycosyl hydrolase enzymes. However, glycans of the human vaginal epithelial surface have not been studied in detail. Here, we elucidate key characteristics of the "normal" vaginal epithelial glycan landscape and analyze the impact of resident microbes on the surface glycocalyx. In human BV, glycocalyx staining was visibly diminished in electron micrographs compared to controls. Biochemical and mass spectrometric analysis showed that, compared to normal vaginal epithelial cells, BV cells were depleted of sialylated N- and O-glycans, with underlying galactose residues exposed on the surface. Treatment of primary epithelial cells from BV-negative women with recombinant Gardnerella sialidases generated BV-like glycan phenotypes. Exposure of cultured VK2 vaginal epithelial cells to recombinant Gardnerella sialidase led to desialylation of glycans and induction of pathways regulating cell death, differentiation, and inflammatory responses. These data provide evidence that vaginal epithelial cells exhibit an altered glycan landscape in BV and suggest that BV-associated glycosidic enzymes may lead to changes in epithelial gene transcription that promote cell turnover and regulate responses toward the resident microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
Dr. Amanda Lewis is on the scientific advisory board of GlycoNet. Dr. Carlito B. Lebrilla is a co-founder and consultant for Infinant Health, InterVenn Bio, and BCD Bioscience. He is also a consultant for Turtle Tree. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Callahan BJ, DiGiulio DB, Goltsman DSA, Sun CL, Costello EK, Jeganathan P, Biggio JR, Wong RJ, Druzin ML, Shaw GM, Stevenson DK, Holmes SP, Relman DA, Replication and refinement of a vaginal microbial signature of preterm birth in two racially distinct cohorts of US women. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114, 9966–9971 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Witkin SS, Linhares IM, Why do lactobacilli dominate the human vaginal microbiota? BJOG 124, 606–611 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Kroon SJ, Ravel J, Huston WM, Cervicovaginal microbiota, women's health, and reproductive outcomes. Fertil Steril 110, 327–336 (2018). - PubMed

