Estimating the efficacy of pharmacogenomics over a lifetime
- PMID: 38020121
- PMCID: PMC10645151
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1006743
Estimating the efficacy of pharmacogenomics over a lifetime
Abstract
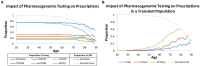
It is well known that common variants in specific genes influence drug metabolism and response, but it is currently unknown what fraction of patients are given prescriptions over a lifetime that could be contraindicated by their pharmacogenomic profiles. To determine the clinical utility of pharmacogenomics over a lifetime in a general patient population, we sequenced the genomes of 300 deceased Marshfield Clinic patients linked to lifelong medical records. Genetic variants in 33 pharmacogenes were evaluated for their lifetime impact on drug prescribing using extensive electronic health records. Results show that 93% of the 300 deceased patients carried clinically relevant variants. Nearly 80% were prescribed approximately three medications on average that may have been impacted by these variants. Longitudinal data suggested that the optimal age for pharmacogenomic testing was prior to age 50, but the optimal age is greatly influenced by the stability of the population in the healthcare system. This study emphasizes the broad clinical impact of pharmacogenomic testing over a lifetime and demonstrates the potential application of genomic medicine in a general patient population for the advancement of precision medicine.
Keywords: Pharmacogenenomics and personalised medicine; drug responce; electronic health record (EHR); individualized medicine; precision medicine.
Copyright © 2023 Ye, Mayer, Leary, Kitchner, Dart, Brilliant and Hebbring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- US-FDA . Table of pharmacogenomic biomarkers in drug labeling (2015) (Accessed May 20, 2015). Available at: http://www.fda.gov/drugs/scienceresearch/researchareas/pharmacogenetics/...
-
- PharmGKB . CPIC Genes/Drugs (2015) Available at: https://www.pharmgkb.org/cpic/pairs
-
- Ji Y, Skierka JM, Blommel JH, Moore BE, VanCuyk DL, Bruflat JK, et al. . Preemptive pharmacogenomic testing for precision medicine: a comprehensive analysis of five actionable pharmacogenomic genes using next-generation DNA sequencing and a customized CYP2D6 genotyping cascade. J Mol Diagn. (2016) 18:438–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2016.01.003, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pulley JM, Denny JC, Peterson JF, Bernard GR, Vnencak-Jones CL, Ramirez AH, et al. . Operational implementation of prospective genotyping for personalized medicine: the design of the Vanderbilt PREDICT project. Clin Pharmacol Ther. (2012) 92:87–95. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2011.371, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

