Metabolic coupling in phyllodes tumor of the breast and its association with tumor progression
- PMID: 38020291
- PMCID: PMC10660424
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2023.14132
Metabolic coupling in phyllodes tumor of the breast and its association with tumor progression
Abstract
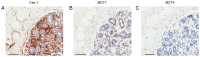
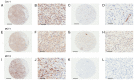
There are markers of metabolic coupling in breast cancer. Loss of caveolin-1 (Cav-1) and upregulation of monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs), especially MCT1 and MCT4, serve an important role in metabolic coupling necessary for release and uptake of metabolites. However, the occurrence of these phenomena in phyllodes tumors (PTs) of the breast is unclear. A total of 101 PTs (60 benign, 26 borderline and 15 malignant) and nine breast tissue samples with no pathological lesions were analyzed. Immunohistochemical staining for Cav-1, MCT1 and MCT4 was performed using tissue microarray and their expression in both stromal and epithelial components was assessed. Cav-1 expression in PTs demonstrated a significant decrease in the stromal component compared with that in the normal breast tissues (P<0.001). MCT1 expression in both epithelial and stromal components was significantly increased in PTs, compared with that in normal breast tissues (both P<0.001). Stromal MCT1 and MCT4 expression were different depending on tumor grade of PTs, and stromal MCT1 expression significantly increased with increasing tumor grade (P<0.001). Although not statistically significant, stromal Cav-1 expression notably decreased with increases in PT grade. High stromal MCT1 expression was significantly associated with lower disease-free survival rate in comparison with low stromal MCT1 expression (P<0.05). These results suggested that changes in protein expression of Cav-1, MCT1 and MCT4 may be associated with tumorigenesis and progression of PTs of the breast.
Keywords: caveolin-1; metabolic coupling; monocarboxylate transporter 1; monocarboxylate transporter 4; phyllodes tumor.
Copyright: © Kim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Allison KH, Brogi E, Ellis IO, Fox SB, Morris EA, Sahin A, Salgado R, Sapino A, Sasano H, Schnitt SJ, et al. Breast tumors. 5th edition. IARC Press; Lyon: 2019. World Health Organization classification of tumours editorial board.
-
- Hoda SA, Brogi E, Koerner FC, Rosen PP. 4th edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: 2014. Rosen's Breast Pathology.
-
- Spitaleri G, Toesca A, Botteri E, Bottiglieri L, Rotmensz N, Boselli S, Sangalli C, Catania C, Toffalorio F, Noberasco C, et al. Breast phyllodes tumor: A review of literature and a single center retrospective series analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013;88:427–436. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.06.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fede ÂBS, Pereira Souza R, Doi M, De Brot M, Aparecida Bueno de Toledo Osorio C, Rocha Melo Gondim G, Casali-da-Rocha JC, Jbili R, Bitencourt AGV, Alves de Souza J, et al. Malignant pyllodes tumor of the breast: A practice review. Clin Pract. 2021;11:205–215. doi: 10.3390/clinpract11020030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
