Kinetic modelling of sterol transport between plasma membrane and endo-lysosomes based on quantitative fluorescence and X-ray imaging data
- PMID: 38020900
- PMCID: PMC10644255
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1144936
Kinetic modelling of sterol transport between plasma membrane and endo-lysosomes based on quantitative fluorescence and X-ray imaging data
Abstract
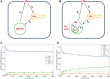
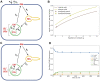
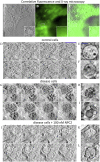
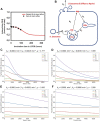
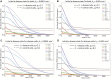
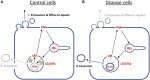
Niemann Pick type C1 and C2 (NPC1 and NPC2) are two sterol-binding proteins which, together, orchestrate cholesterol transport through late endosomes and lysosomes (LE/LYSs). NPC2 can facilitate sterol exchange between model membranes severalfold, but how this is connected to its function in cells is poorly understood. Using fluorescent analogs of cholesterol and quantitative fluorescence microscopy, we have recently measured the transport kinetics of sterol between plasma membrane (PM), recycling endosomes (REs) and LE/LYSs in control and NPC2 deficient fibroblasts. Here, we use kinetic modeling of this data to determine rate constants for sterol transport between intracellular compartments. Our model predicts that sterol is trapped in intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) of LE/LYSs in the absence of NPC2, causing delayed sterol export from LE/LYSs in NPC2 deficient fibroblasts. Using soft X-ray tomography, we confirm, that LE/LYSs of NPC2 deficient cells but not of control cells contain enlarged, carbon-rich intraluminal vesicular structures, supporting our model prediction of lipid accumulation in ILVs. By including sterol export via exocytosis of ILVs as exosomes and by release of vesicles-ectosomes-from the PM, we can reconcile measured sterol efflux kinetics and show that both pathways can be reciprocally regulated by the intraluminal sterol transfer activity of NPC2 inside LE/LYSs. Our results thereby connect the in vitro function of NPC2 as sterol transfer protein between membranes with its in vivo function.
Keywords: Niemann-Pick disease type C2; X-ray microscopy; cholesterol efflux; differential equations; diffusion; kinetic modelling; sterol; time-delay.
Copyright © 2023 Wüstner, Dupont Juhl, Egebjerg, Werner, McNally and Schneider.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Niemann Pick C2 protein enables cholesterol transfer from endo-lysosomes to the plasma membrane for efflux by shedding of extracellular vesicles.Chem Phys Lipids. 2021 Mar;235:105047. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2020.105047. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Chem Phys Lipids. 2021. PMID: 33422548
-
Niemann-Pick C2 protein regulates sterol transport between plasma membrane and late endosomes in human fibroblasts.Chem Phys Lipids. 2018 Jul;213:48-61. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2018.03.006. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Chem Phys Lipids. 2018. PMID: 29580834
-
Quantitative imaging of membrane contact sites for sterol transfer between endo-lysosomes and mitochondria in living cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 26;11(1):8927. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87876-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33903617 Free PMC article.
-
Niemann-Pick C2 (NPC2) and intracellular cholesterol trafficking.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jul;1791(7):671-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.02.001. Epub 2009 Feb 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19232397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and consequences of impaired lipid trafficking in Niemann-Pick type C1-deficient mammalian cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jul;1791(7):659-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.01.025. Epub 2009 Feb 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19416638 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

