Time domain diffuse Raman spectroscopy using single pixel detection
- PMID: 38021118
- PMCID: PMC10659806
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.502022
Time domain diffuse Raman spectroscopy using single pixel detection
Abstract
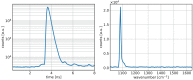
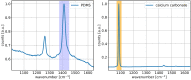
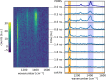
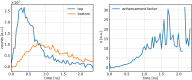
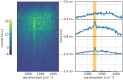
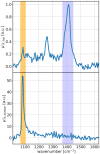
Diffuse Raman spectroscopy (DIRS) extends the high chemical specificity of Raman scattering to in-depth investigation of thick biological tissues. We present here a novel approach for time-domain diffuse Raman spectroscopy (TD-DIRS) based on a single-pixel detector and a digital micromirror device (DMD) within an imaging spectrometer for wavelength encoding. This overcomes the intrinsic complexity and high cost of detection arrays with ps-resolving time capability. Unlike spatially offset Raman spectroscopy (SORS) or frequency offset Raman spectroscopy (FORS), TD-DIRS exploits the time-of-flight distribution of photons to probe the depth of the Raman signal at a single wavelength with a single source-detector separation. We validated the system using a bilayer tissue-bone mimicking phantom composed of a 1 cm thick slab of silicone overlaying a calcium carbonate specimen and demonstrated a high differentiation of the two Raman signals. We reconstructed the Raman spectra of the two layers, offering the potential for improved and quantitative material analysis. Using a bilayer phantom made of porcine muscle and calcium carbonate, we proved that our system can retrieve Raman peaks even in the presence of autofluorescence typical of biomedical tissues. Overall, our novel TD-DIRS setup proposes a cost-effective and high-performance approach for in-depth Raman spectroscopy in diffusive media.
© 2023 Optica Publishing Group under the terms of the Optica Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Conti C., Botteon A., Colombo C., Pinna D., Realini M., Matousek P., “Advances in Raman spectroscopy for the non-destructive subsurface analysis of artworks: Micro-SORS,” (2020).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
