Case Series of Demodicosis in Acne Vulgaris Patients
- PMID: 38021431
- PMCID: PMC10664713
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S441581
Case Series of Demodicosis in Acne Vulgaris Patients
Abstract
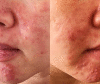
An abnormal density of Demodex mites can trigger many skin disorders known as demodicosis. Clinical manifestations of demodicosis may resemble other skin diseases and can coexist with other skin disorders, resulting in underdiagnosis and a more challenging diagnosis. Here, we report three cases of demodicosis in acne vulgaris patients. These case series have discussed their clinical features along with optimal strategies for diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: Demodex; acne vulgaris; demodicosis; mite; rosacea.
© 2023 Paichitrojjana and Paichitrojjana.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

