Recurrence of Pigmented Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma of the Kidney With Xp11 Translocation: A Case Report
- PMID: 38021949
- PMCID: PMC10656598
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.47305
Recurrence of Pigmented Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma of the Kidney With Xp11 Translocation: A Case Report
Abstract
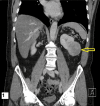
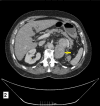
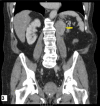
This case report pertains to a 70-year-old male patient with a medical history marked by atrial fibrillation, ankylosing spondylitis, and Crohn's disease. Eight years prior, the patient underwent a left radical nephrectomy due to the presence of a pigmented epithelioid angiomyolipoma (PEComa) in the kidney. Notably, pathological examination revealed an unusual subtype of PEComa characterized by Xp11 gene translocation, indicating a more aggressive clinical profile. Following a five-year observation period without recurrence, the patient was discharged. However, eight years after initial treatment, he presented with vague symptoms of left loin discomfort and fullness, which had persisted for several weeks. Subsequent evaluation via computed tomography (CT) scanning showed a small lesion at the site of the renal bed. Surgical resection confirmed the return of the identical tumour. Key clinical points elucidated by this case include the varied behaviour of PEComas, the essential need for prolonged surveillance, and a recognition that recurrences can transpire even after extended disease-free intervals. Prior studies suggest recurrence rates of up to 31.8% for this specific PEComa subtype, emphasising the requirement for prolonged follow-up protocols.
Keywords: adequate follow-up; laproscopic nephrectomy; local excision; renal malignant epithelioid angiomyolipoma; xp11 translocation pecoma.
Copyright © 2023, Srour et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dia-gnostic Challenges and Extraordinary Treatment Response in Rare Malignant PEComa Tumor of the Kidney.Klin Onkol. 2018 Fall;31(6):448-452. doi: 10.14735/amko2018448. Klin Onkol. 2018. PMID: 30545225 English.
-
Primary Xp11 translocation PEComa of the testis with SFPQ⁃TFE3 rearrangement: a case report and review of the literature.Diagn Pathol. 2023 Jan 16;18(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13000-023-01288-x. Diagn Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36647137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic pitfall of a rare variant of angiomyolipoma, epithelioid angiomyolipoma - a case report.Pan Afr Med J. 2020 Nov 2;37:210. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2020.37.210.26269. eCollection 2020. Pan Afr Med J. 2020. PMID: 33505578 Free PMC article.
-
Malignant melanotic Xp11 neoplasms exhibit a clinicopathologic spectrum and gene expression profiling akin to alveolar soft part sarcoma: a proposal for reclassification.J Pathol. 2020 Aug;251(4):365-377. doi: 10.1002/path.5470. Epub 2020 Jul 2. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32418203
-
Primary Epithelioid Angiomyolipoma of Adrenal Gland: Case Report and Literature Review.Prague Med Rep. 2022;123(3):199-205. doi: 10.14712/23362936.2022.19. Prague Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 36107449 Review.
References
-
- A distinctive subset of PEComas harbors TFE3 gene fusions. Argani P, Aulmann S, Illei PB, et al. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:1395–1406. - PubMed
-
- Pigmented perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) of the kidney: a case report and review of the literature. Chang H, Jung W, Kang Y, Jung WY. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23136579/. Korean J Pathol. 2012;46:499–502. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clinical and pathological features of renal epithelioid angiomyolipoma (PEComa): a single institution series. Saoud R, Kristof TW, Judge C, Chumbalkar V, Antic T, Eggener S, Modi P. Urol Oncol. 2022;40:18–24. - PubMed
-
- Malignant melanotic Xp11 neoplasms exhibit a clinicopathologic spectrum and gene expression profiling akin to alveolar soft part sarcoma: a proposal for reclassification. Wang XT, Fang R, Zhang RS, et al. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5470. J Pathol. 2020;251:365–377. - PubMed
-
- Primary Xp11 translocation PEComa of the testis with SFPQ⁃TFE3 rearrangement: a case report and review of the literature. Zhang H, Wang S, Meng L. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-023-01288-x. Diagn Pathol. 2023;18:6. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
