Two case reports: EML4-ALK rearrangement large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and literature review
- PMID: 38023218
- PMCID: PMC10646488
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1227980
Two case reports: EML4-ALK rearrangement large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and literature review
Abstract
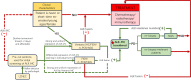
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene (ALK) rearrangement is present in only approximately 5% of non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) and is scarce in LCNEC patients. The conventional first-line treatment options are chemotherapy combined with immunotherapy or chemotherapy followed by palliative radiotherapy. In this report, we present two cases of metastatic LCNEC with EML4-ALK fusion that were treated with ALK-TKI inhibitors and demonstrated a rapid therapeutic response. Both patients were nonsmoking women who declined cytotoxic chemotherapy, underwent Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), and confirmed EML4-ALK fusion. They were treated with alectinib as first-line therapy, and the tumors showed significant shrinkage after two months, achieving a PR (defined as a more than 30% decrease in the sum of maximal dimensions). The PFS was 22 months and 32 months, respectively, until the last follow-up. A systematic review of all previously reported cases of LCNEC with ALK mutations identified only 21 cases. These cases were characterized by being female (71.4%), nonsmoking (85.7%), diagnosed at a relatively young age (median age 51.1), and stage IV (89.5%), with an overall response rate (ORR) of 90.5%. PFS and OS were significantly longer than those treated with conventional chemotherapy/immunotherapy. Based on the clinical characteristics and the effective therapeutic outcomes with ALK inhibitors in LCNEC patients with ALK fusion, we recommend routine ALK IHC (economical, affordable, and convenient, but with higher false positives) as a screening method in advanced LCNEC patients, particularly nonsmoking females or those who are not candidates for or unwilling to undergo cytotoxic chemotherapy. Further molecular profiling is necessary to confirm these potential beneficiaries. We suggest TKI inhibitors as the first-line treatment for metastatic LCNEC with ALK fusion. Additional studies on larger cohorts are required to assess the prevalence of ALK gene fusions and their sensitivity to various ALK inhibitors.
Keywords: ALK-TKI inhibitor; EML4-ALK rearrangement; alectinib; immunohistochemistry; large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Zhang, Wang, Zong, Sun, Qin and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
EML4-ALK rearrangement of lung large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: a case report.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Jan 31;11(2):134. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-6062. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36819595 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ALK in Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Lung.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 7;12:911294. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.911294. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35756632 Free PMC article.
-
Use of ALK Immunohistochemistry for Optimal Therapeutic Strategy of Pulmonary Large-cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma and Identification of a Novel KIF5B-ALK Fusion Oncokinase.Anticancer Res. 2019 Jan;39(1):413-420. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13127. Anticancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30591488
-
Mixed responses to first-line alectinib in non-small cell lung cancer patients with rare ALK gene fusions: A case series and literature review.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Oct;25(19):9476-9481. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16897. Epub 2021 Sep 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34541785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 8;22(2):593. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020593. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33435596 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Refining Criteria for Choosing the First-Line Treatment for Real-World Patients with Advanced ALK-Rearranged NSCLC.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 21;26(13):5969. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135969. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[A Case of Multiple Primary Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Carcinoma with EML4-ALK Fusion Gene Positive].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2025 Mar 20;28(3):230-236. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2025.102.10. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40210483 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Dramatic Response to Ensartinib in Metastatic Neuroendocrine Tumors With a Novel CEP44-ALK Fusion: A Case Report and Literature Review.Clin Respir J. 2024 Dec;18(12):e70040. doi: 10.1111/crj.70040. Clin Respir J. 2024. PMID: 39667359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung Carcinoid Tumors With Potentially Actionable Genomic Alterations and Responses to Targeted Therapies.Clin Lung Cancer. 2025 Jul;26(5):354-363.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2025.03.009. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Clin Lung Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40234130 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the complexity of EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma: a unique case report with histological transformations and co-alteration acquisition.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 28;14(2):639-648. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-707. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40114956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Derks JL, Leblay N, Lantuejoul S, Dingemans AC, Speel EM, Fernandez-Cuesta L. New insights into the molecular characteristics of pulmonary carcinoids and large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas, and the impact on their clinical management. J Thorac Oncol. (2018) 13(6):752–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

