Ectopic Tooth with Odontogenic Keratocyst in Myasthenia Gravis: A Rare Coexistence
- PMID: 38023599
- PMCID: PMC10666839
- DOI: 10.4103/ijabmr.ijabmr_4_23
Ectopic Tooth with Odontogenic Keratocyst in Myasthenia Gravis: A Rare Coexistence
Abstract
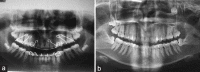
Ectopic tooth in nondentate areas is uncommon. Odontogenic keratocyst arising from impacted tooth in the inferior border of orbit is very rare. This article reports the case of a 22-year-old female with odontogenic keratocyst arising from an impacted left maxillary third molar in the inferior border of the orbit causing symptoms of chronic sinusitis. The patient also had myasthenia gravis which confounded the diagnosis. The cyst was surgically enucleated along with the tooth which relieved the symptoms of the patient.
Keywords: Chronic sinusitis; ectopic tooth; impacted maxillary third molar; odontogenic keratocyst cyst.
Copyright: © 2023 International Journal of Applied and Basic Medical Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- O¨mezli MM, Ayranci F, Yurtyapan H, Salman N. Dentigerous cyst associated with an ectopic tooth in the subcondylar area: A case report and literature review. Middle Black Sea J Health Sci. 2015;1:21–6.
-
- Di Pasquale P, Shermetaro C. Endoscopic removal of a dentigerous cyst producing unilateral maxillary sinus opacification on computed tomography. Ear Nose Throat J. 2006;85:747–8. - PubMed
-
- Demirtas N, Kazancioglu HO, Ezirganli S. Ectopic tooth in the maxillary sinus diagnosed with an ophthalmic complication. J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25:e351–2. - PubMed
-
- Silva GC, Silva EC, Santiago Gomez R, Vieira TC. Odontogenic keratocyst in the maxillary sinus: Report of two cases. Oral Oncol. 2006;42:231–4.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
