Prediction of drug permeation through microneedled skin by machine learning
- PMID: 38023708
- PMCID: PMC10658566
- DOI: 10.1002/btm2.10512
Prediction of drug permeation through microneedled skin by machine learning
Abstract
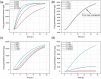
Stratum corneum is the outermost layer of the skin preventing external substances from entering human body. Microneedles (MNs) are sharp protrusions of a few hundred microns in length, which can penetrate the stratum corneum to facilitate drug permeation through skin. To determine the amount of drug delivered through skin, in vitro drug permeation testing is commonly used, but the testing is costly and time-consuming. To address this issue, machine learning methods were employed to predict drug permeation through the skin, circumventing the need of conducting skin permeation experiments. By comparing the experimental data and simulated results, it was found extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) was the best among the four simulation methods. It was also found that drug loading, permeation time, and MN surface area were critical parameters in the models. In conclusion, machine learning is useful to predict drug permeation profiles for MN-facilitated transdermal drug delivery.
Keywords: XGBoost; machine learning; microneedle; multiple linear regression; random forest; transdermal.
© 2023 The Authors. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Lim SH, Kathuria H, Amir MHB, et al. High resolution photopolymer for 3D printing of personalised microneedle for transdermal delivery of anti‐wrinkle small peptide. J Control Release. 2021;329:907‐918. - PubMed
-
- Shan J, Zhang X, Kong B, et al. Coordination polymer nanozymes‐integrated colorimetric microneedle patches for intelligent wound infection management. J Chem Eng. 2022;444:136640.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

