The rice SnRK family: biological roles and cell signaling modules
- PMID: 38023908
- PMCID: PMC10644236
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1285485
The rice SnRK family: biological roles and cell signaling modules
Abstract
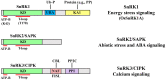
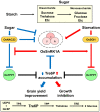
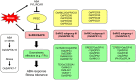
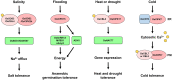
Stimulus-activated signaling pathways orchestrate cellular responses to control plant growth and development and mitigate the effects of adverse environmental conditions. During this process, signaling components are modulated by central regulators of various signal transduction pathways. Protein phosphorylation by kinases is one of the most important events transmitting signals downstream, via the posttranslational modification of signaling components. The plant serine and threonine kinase SNF1-related protein kinase (SnRK) family, which is classified into three subgroups, is highly conserved in plants. SnRKs participate in a wide range of signaling pathways and control cellular processes including plant growth and development and responses to abiotic and biotic stress. Recent notable discoveries have increased our understanding of how SnRKs control these various processes in rice (Oryza sativa). In this review, we summarize current knowledge of the roles of OsSnRK signaling pathways in plant growth, development, and stress responses and discuss recent insights. This review lays the foundation for further studies on SnRK signal transduction and for developing strategies to enhance stress tolerance in plants.
Keywords: SNF1-related protein kinase; abiotic stress; biotic stress; cell signaling; phosphorylation; plant growth and development; rice.
Copyright © 2023 Son and Park.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The multifaceted role of different SnRK gene family members in regulating multiple abiotic stresses in plants.Physiol Plant. 2024 Sep-Oct;176(5):e14543. doi: 10.1111/ppl.14543. Physiol Plant. 2024. PMID: 39403065 Review.
-
Evolution of TOR-SnRK dynamics in green plants and its integration with phytohormone signaling networks.J Exp Bot. 2019 Apr 15;70(8):2239-2259. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz107. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 30870564 Review.
-
Genome-wide analysis of SnRK gene family in Brachypodium distachyon and functional characterization of BdSnRK2.9.Plant Sci. 2015 Aug;237:33-45. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.05.008. Epub 2015 May 18. Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26089150
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Expression Pattern and Sequence Variation Analysis of SnRK Family Genes in Barley.Plants (Basel). 2022 Apr 3;11(7):975. doi: 10.3390/plants11070975. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406955 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of sucrose nonfermenting-1-related protein kinase (SnRK) genes in barley and RNA-seq analyses of their expression in response to abscisic acid treatment.BMC Genomics. 2021 Apr 26;22(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07601-6. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33902444 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification of ZmMYC2 binding sites and target genes in maize.BMC Genomics. 2024 Apr 23;25(1):397. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10297-z. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38654166 Free PMC article.
-
Grain under pressure: Harnessing biochemical pathways to beat drought and heat in wheat.Plant J. 2025 Jun;122(6):e70253. doi: 10.1111/tpj.70253. Plant J. 2025. PMID: 40532117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic signatures of SnRKs highlighted conserved evolution within orchids and stress responses through ABA signaling in the Cymbidium ensifolium.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Mar 3;25(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06280-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40025443 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

