Paediatric and Adolescent Breast Cancer: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 38024017
- PMCID: PMC10656636
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.48983
Paediatric and Adolescent Breast Cancer: A Narrative Review
Abstract
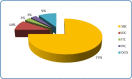
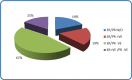
Breast cancer is the most prevalent form of cancer worldwide. Every year, it affects a significant number of women in the UK and is considered one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths globally. While breast cancer is primarily linked to adult women, its occurrence in children and adolescents is exceedingly rare. This study conducted a narrative review spanning from 1999 to 2023, examining 32 case reports to investigate the characteristics of breast cancer in the paediatric age group. These reports focused on patients under 18 years old who were diagnosed with primary glandular breast cancer, excluding cases originating from other tissues like angiosarcoma, leukaemia, and metastatic cancer. The data analysis encompassed various parameters, including gender, age, histology, receptor status, lymph node involvement, treatment methods, and genetic characteristics. From the published case reports, it was concluded that the most common type of breast cancer affecting children and adolescents is secretory breast carcinoma and predominantly occurs in females. It is typically hormone receptors negative, and the preferred treatment approach involves mastectomy as breast conservation surgery to preserve the developing breast tissue is a real challenge due to limited breast tissue volume in this age group.
Keywords: brca gene mutation; etv6-ntrk3 fusion gene; mastectomy; paediatric breast cancer; secretory breast carcinoma.
Copyright © 2023, Hassan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- The Oncotype DX Recurrence Score's Impact on the management of oestrogen-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative, low-burden axillary status breast cancer (REHAB study): results of a single centre. Saad Abdalla Al-Zawi A, Yin SL, Mahmood B, Jalil A, Aladili Z. Cureus. 2022;14:0. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Malignant breast cancer in children: a review of 75 patients. Gutierrez JC, Housri N, Koniaris LG, Fischer AC, Sola JE. J Surg Res. 2008;147:182–188. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
