Effect of Thrombolysis on Circulating Microparticles in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 38024103
- PMCID: PMC10676276
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/5559368
Effect of Thrombolysis on Circulating Microparticles in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Objective: We demonstrated that circulating microparticles (MPs) are increased in patients with coronary heart disease (both chronic coronary syndrome (CCS) and acute coronary syndrome). Whether thrombolysis affects MPs in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) with or without percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is unknown.
Methods: This study was divided into three groups: STEMI patients with thrombolysis (n = 18) were group T, patients with chronic coronary syndrome (n = 20) were group CCS, and healthy volunteers (n = 20) were the control group. Fasting venous blood was extracted from patients in the CCS and control groups, and venous blood was extracted from patients in the T group before (pre-T) and 2 hours after (post-T) thrombolysis. MPs from each group were obtained by centrifugation. After determining the concentration, the effects of MPs on endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in rat myocardial tissue in vitro were detected by immunohistochemistry and western blotting. Changes in nitric oxide (NO) and oxygen free radicals (O2•-) were also detected. The effect of MPs on vasodilation in isolated rat thoracic aortae was detected.
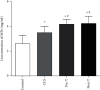
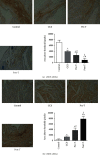
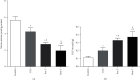
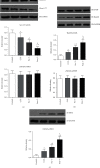
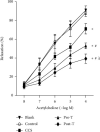
Results: Compared with that in the control group (2.60 ± 0.38 mg/ml), the concentration of MPs was increased in patients with CCS (3.49 ± 0.72 mg/ml) and in STEMI patients before thrombolysis (4.17 ± 0.58 mg/ml). However, thrombolysis did not further increase MP levels (post-T, 4.23 ± 1.01 mg/ml) compared with those in STEMI patients before thrombolysis. Compared with those in the control group, MPs in both CCS and STEMI patients before thrombolysis inhibited the expression of eNOS (both immunohistochemistry and western blot analysis of phosphorylation at Ser1177), NO production in the isolated myocardium and vasodilation in vitro and stimulated the expression of iNOS (immunohistochemistry and western blot analysis of phosphorylation at Thr495), and the generation of O2•- in the isolated myocardium. The effects of MPs were further enhanced by MPs from STEMI patients 2 hours after thrombolysis.
Conclusion: Changes in MP function after thrombolysis may be one of the mechanisms leading to ischemia-reperfusion after thrombolysis.
Copyright © 2023 Zhe Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microparticles from Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Impair Vasodilatation by Uncoupling Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase.Shock. 2017 Aug;48(2):201-208. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000823. Shock. 2017. PMID: 28002238 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of a Pharmaco-Invasive Strategy With Half-Dose Alteplase Versus Primary Angioplasty in ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: EARLY-MYO Trial (Early Routine Catheterization After Alteplase Fibrinolysis Versus Primary PCI in Acute ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction).Circulation. 2017 Oct 17;136(16):1462-1473. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030582. Epub 2017 Aug 27. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28844990 Clinical Trial.
-
Measurement of microvascular function in patients presenting with thrombolysis for ST elevation myocardial infarction, and PCI for non-ST elevation myocardial infarction.Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2018 Dec;19(8):917-922. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2018. PMID: 29709534
-
Use of ticagrelor alongside fibrinolytic therapy in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: Practical perspectives based on data from the TREAT study.Clin Cardiol. 2018 Oct;41(10):1322-1327. doi: 10.1002/clc.23043. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Clin Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 30098028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombolytic Therapy for ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Presenting to non-Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Centers During the COVID-19 Crisis.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2021 Sep 28;23(10):152. doi: 10.1007/s11886-021-01576-2. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34585300 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Time to Treatment Delay and Clinical Indicators in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Descriptive Cross-sectional Study.J Caring Sci. 2024 Aug 4;13(4):286-293. doi: 10.34172/jcs.33506. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Caring Sci. 2024. PMID: 39974833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ibanez B., James S., Agewall S., et al. 2017 ESC guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: the task force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) European Heart Journal . 2018;39(2):119–177. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx393. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
