A systematic mapping review of links between handling wild meat and zoonotic diseases
- PMID: 38024256
- PMCID: PMC10665173
- DOI: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2023.100637
A systematic mapping review of links between handling wild meat and zoonotic diseases
Abstract
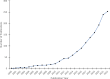
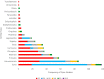
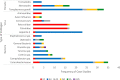
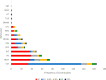
1.Hunting, trade, and consumption of wildlife present a serious threat to global public health as it places humans in close contact with zoonotic pathogens.2.We systematically mapped the literature on wild meat handling and zoonotic disease transmission (1996-2022) using the online database Web of Science and Google search engine and identified 6229 articles out of which 253 were finally selected for use in our mapping review; 51 of these provided specific information regarding transmission risks.3.The reviewed studies reported 43 zoonotic pathogens (17 bacteria, 15 viruses, and 11 parasites) that could pose a potential risk to human health.4.Sixteen hygienic and sanitary behaviours were described in the reviewed studies. Disease surveillance was the most frequent. Most of the surveillance studies were carried out in Europe and were less common in the tropics.5.To inform policy and practical actions effectively, it is imperative to broaden our understanding of how various mitigation behaviours can be employed to minimize the risk of transmission.
Keywords: Bushmeat; Disease prevention; Food-borne disease; Hunting; Meat handling.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pekar J.E., Magee A., Parker E., Moshiri N., Izhikevich K., Havens J.L., Gangavarapu K., Malpica Serrano L.M., Crits-Christoph A., Matteson N.L., Zeller M., Levy J.I., Wang J.C., Hughes S., Lee J., Park H., Park M.-S., Ching Zi Yan K., Lin R.T.P., Mat Isa M.N., Noor Y.M., Vasylyeva T.I., Garry R.F., Holmes E.C., Rambaut A., Suchard M.A., Andersen K.G., Worobey M., Wertheim J.O. The molecular epidemiology of multiple zoonotic origins of SARS-CoV-2. Science. 2022;377:960–966. doi: 10.1126/science.abp8337. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Worobey M., Levy J.I., Malpica Serrano L., Crits-Christoph A., Pekar J.E., Goldstein S.A., Rasmussen A.L., Kraemer M.U.G., Newman C., Koopmans M.P.G., Suchard M.A., Wertheim J.O., Lemey P., Robertson D.L., Garry R.F., Holmes E.C., Rambaut A., Andersen K.G. The Huanan seafood wholesale market in Wuhan was the early epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic. Science. 2022;377:951–959. doi: 10.1126/science.abp8715. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Newell D.G., Koopmans M., Verhoef L., Duizer E., Aidara-Kane A., Sprong H., Opsteegh M., Langelaar M., Threfall J., Scheutz F., van der Giessen J., Kruse H. Food-borne diseases -– the challenges of 20 years ago still persist while new ones continue to emerge. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010;139(Suppl. 1):S3–15. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.01.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization; 2015. WHO Estimates of the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases: Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group 2007-2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

