A synergistic investigation of azo-thiazole derivatives incorporating thiazole moieties: a comprehensive exploration of their synthesis, characterization, computational insights, solvatochromism, and multimodal biological activity assessment
- PMID: 38024963
- PMCID: PMC10668576
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra06469g
A synergistic investigation of azo-thiazole derivatives incorporating thiazole moieties: a comprehensive exploration of their synthesis, characterization, computational insights, solvatochromism, and multimodal biological activity assessment
Abstract
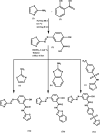
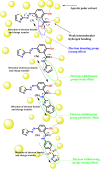
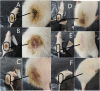
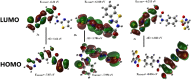
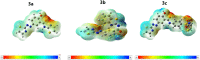
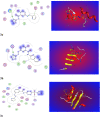
In the present study, a novel series of azo-thiazole derivatives (3a-c) containing a thiazole moiety was successfully synthesized. The structure of these derivatives was examined by spectroscopic techniques, including 1H NMR, 13C NMR, FT-IR, and HRMS. Further, the novel synthesized compounds were evaluated for their in vitro biological activities, such as antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities, and an in silico study was performed. The antibacterial results demonstrated that compounds 3a and 3c (MIC = 10 μg mL-1) have a notable potency against Staphylococcus aureus compared to azithromycin (MIC = 40 μg mL-1). Alternatively, compound 3b displayed a four-fold higher potency (24 recovery days, 1.83 mg day-1) than Hamazine (28 recovery days, 4.14 mg day-1) in promoting burn wound healing, and it also exhibited a comparable inhibitory activity against screened bacterial pathogens compared to the reference drug. Docking on 1KZN, considering the excellent impact of compounds on the crystal structure of E. coli1KZN, a 24 kDa domain, in complex with clorobiocin, indicated the close binding of compounds 3a-c with the active site of the 1KZN protein, which is consistent with their observed biological activity. Additionally, we conducted molecular dynamics simulations on the docked complexes of compounds 3a-c with 1KZN retrieved from the PDB to assess their stability and molecular interactions. Furthermore, we assessed their electrochemical characteristics via DFT calculations. Employing PASS and pkCSM platforms, we gained insights into controlling the bioactivity and physicochemical features of these compounds, highlighting their potential as new active agents.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors affirm that there are no recognized financial conflicts of interest or personal affiliations that might have seemed to affect the findings reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synthesis, antibacterial activity, synergistic effect, cytotoxicity, docking and molecular dynamics of benzimidazole analogues.Comput Biol Chem. 2018 Oct;76:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2018.05.021. Epub 2018 May 24. Comput Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29857255
-
Synthesis of Isatin Derivatives Exhibiting Antibacterial, Antifungal and Cytotoxic Activities.Curr Org Synth. 2022 Aug 6;19(6):748-756. doi: 10.2174/1570179419666220128091313. Curr Org Synth. 2022. PMID: 35088673
-
Synthesis, characterization, biological activities, and computational studies of pyrazolyl-thiazole derivatives of thiophene.RSC Adv. 2024 Dec 10;14(52):39004-39016. doi: 10.1039/d4ra06228k. eCollection 2024 Dec 3. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39659609 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial activity of novel 5-benzylidene-3-(3-phenylallylideneamino)imidazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives causing clinical pathogens: Synthesis and molecular docking studies.J Infect Public Health. 2020 Dec;13(12):1951-1960. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.09.017. Epub 2020 Oct 21. J Infect Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33289644
-
Synthesis, antimicrobial, SAR, PASS, molecular docking, molecular dynamics and pharmacokinetics studies of 5'-O-uridine derivatives bearing acyl moieties: POM study and identification of the pharmacophore sites.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2022;41(10):1036-1083. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2022.2096898. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 35797068
Cited by
-
Design, synthesis, and computational analysis (molecular docking, DFT, MEP, RDG, ELF) of diazepine and oxazepine sulfonamides: biological evaluation for in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and cytotoxicity predictions.Mol Divers. 2025 Jun;29(3):2367-2389. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10996-5. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 39356365
-
Efficient synthesis of N-(ethylcarbamothioyl)-1-naphthamide: X-ray structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis, DFTs, and molecular modelling investigations as selective inhibitor of alkaline phosphatase.BMC Chem. 2025 Jul 2;19(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s13065-025-01525-y. BMC Chem. 2025. PMID: 40605008 Free PMC article.
-
Fluopyram analogues containing an indole moiety: synthesis, biological activity and molecular docking study.Mol Divers. 2025 Jan 20. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11106-9. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 39832082
-
Multifunctional in vitro, in silico and DFT analyses on antimicrobial BagremycinA biosynthesized by Micromonospora chokoriensis CR3 from Hieracium canadense.Sci Rep. 2024 May 14;14(1):10976. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61490-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38745055 Free PMC article.
-
One-pot synthesis of quercetin-functionalized silver and copper nanoparticles for enhanced optical, antimicrobial, and computational properties.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 21;15(1):26391. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12586-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40691496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zheng Z. et al., Design and synthesis optimization of novel diimide indoles derivatives for ameliorating acute lung injury through modulation of NF-κB signaling pathway. Bioorg. Chem. 2023;136:106557. - PubMed
-
- Qiang S. et al., Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel FtsZ-targeted 3-arylalkoxy-2, 6-difluorobenzamides as Potential Antimicrobial Agents. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016;87(2):257–264. - PubMed
-
- Hassan S. A. et al., Design and synthesis of oxazepine derivatives from sulfonamide Schiff bases as antimicrobial and antioxidant agents with low cytotoxicity and hemolytic prospective. J. Mol. Struct. 2023;1292:136121.
-
- Hassan S. A. et al., In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, hemolytic activities and in silico POM/DFT/DNA-binding and pharmacokinetic analyses of new sulfonamide bearing thiazolidin-4-ones. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Hamad H. Q. Taher S. G. Aziz D. M. Synthesis and Molecular Docking Studies of New Series of Bis-Schiff Bases Thiadiazoles Derived From Disulfides and Thioethers with Potent Antibacterial Properties. Science Journal of University of Zakho. 2022;10(3):130–139.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

