The Retinal Ganglion Cell Repopulation, Stem Cell Transplantation, and Optic Nerve Regeneration Consortium
- PMID: 38025164
- PMCID: PMC10630665
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xops.2023.100390
The Retinal Ganglion Cell Repopulation, Stem Cell Transplantation, and Optic Nerve Regeneration Consortium
Abstract
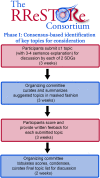
Purpose: The Retinal Ganglion Cell (RGC) Repopulation, Stem Cell Transplantation, and Optic Nerve Regeneration (RReSTORe) consortium was founded in 2021 to help address the numerous scientific and clinical obstacles that impede development of vision-restorative treatments for patients with optic neuropathies. The goals of the RReSTORe consortium are: (1) to define and prioritize the most critical challenges and questions related to RGC regeneration; (2) to brainstorm innovative tools and experimental approaches to meet these challenges; and (3) to foster opportunities for collaborative scientific research among diverse investigators.
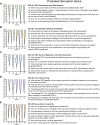
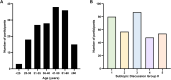
Design and participants: The RReSTORe consortium currently includes > 220 members spanning all career stages worldwide and is directed by an organizing committee comprised of 15 leading scientists and physician-scientists of diverse backgrounds.
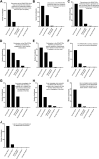
Methods: Herein, we describe the structure and organization of the RReSTORe consortium, its activities to date, and the perceived impact that the consortium has had on the field based on a survey of participants.
Results: In addition to helping propel the field of regenerative medicine as applied to optic neuropathies, the RReSTORe consortium serves as a framework for developing large collaborative groups aimed at tackling audacious goals that may be expanded beyond ophthalmology and vision science.
Conclusions: The development of innovative interventions capable of restoring vision for patients suffering from optic neuropathy would be transformative for the ophthalmology field, and may set the stage for functional restoration in other central nervous system disorders. By coordinating large-scale, international collaborations among scientists with diverse and complementary expertise, we are confident that the RReSTORe consortium will help to accelerate the field toward clinical translation.
Financial disclosures: Proprietary or commercial disclosure may be found in the Footnotes and Disclosures at the end of this article.
Keywords: Collaborative science; Neuroregeneration; Optic neuropathy; Regenerative medicine; Vision restoration.
© 2023 by the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Figures

References
-
- Aguzzi E.A., Zhang K.Y., Nagalingam A., et al. Internal limiting membrane disruption facilitates engraftment of transplanted human stem cell derived retinal ganglion cells. bioRxiv. 2022 doi: 10.1101/2022.12.13.519327. - DOI
Grants and funding
- R01 EY015290/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY028148/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R13 EY034018/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 EY033269/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY030590/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 EY030163/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY030838/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 EY029893/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY036252/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 EY031797/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 EY031801/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EY034332/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY021482/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States

