Seasonal and inter-seasonal RSV activity in the European Region during the COVID-19 pandemic from autumn 2020 to summer 2022
- PMID: 38025589
- PMCID: PMC10661829
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.13219
Seasonal and inter-seasonal RSV activity in the European Region during the COVID-19 pandemic from autumn 2020 to summer 2022
Abstract
Background: The emergence of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in early 2020 and subsequent implementation of public health and social measures (PHSM) disrupted the epidemiology of respiratory viruses. This work describes the epidemiology of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) observed during two winter seasons (weeks 40-20) and inter-seasonal periods (weeks 21-39) during the pandemic between October 2020 and September 2022.
Methods: Using data submitted to The European Surveillance System (TESSy) by countries or territories in the World Health Organization (WHO) European Region between weeks 40/2020 and 39/2022, we aggregated country-specific weekly RSV counts of sentinel, non-sentinel and Severe Acute Respiratory Infection (SARI) surveillance specimens and calculated percentage positivity. Results for both 2020/21 and 2021/22 seasons and inter-seasons were compared with pre-pandemic 2016/17 to 2019/20 seasons and inter-seasons.
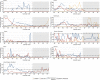
Results: Although more specimens were tested than in pre-COVID-19 pandemic seasons, very few RSV detections were reported during the 2020/21 season in all surveillance systems. During the 2021 inter-season, a gradual increase in detections was observed in all systems. In 2021/22, all systems saw early peaks of RSV infection, and during the 2022 inter-seasonal period, patterns of detections were closer to those seen before the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusion: RSV surveillance continued throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, with an initial reduction in transmission, followed by very high and out-of-season RSV circulation (summer 2021) and then an early start of the 2021/22 season. As of the 2022/23 season, RSV circulation had not yet normalised.
Keywords: COVID‐19 pandemic; Europe; epidemiology; respiratory syncytial virus; severity; surveillance.
© 2023 The Authors. Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The following authors declare having received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI): Adam Meijer (The Netherlands) and Anne Teirlinck (The Netherlands). All other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Li Y, Wang X, Broberg EK, Campbell H, Nair H, European RSV Surveillance Network . Seasonality of respiratory syncytial virus and its association with meteorological factors in 13 European countries, week 40 2010 to week 39 2019. Eurosurveillance. 2022;27(16):2100619. doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.16.2100619 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Broberg EK, Waris M, Johansen K, Snacken R, Penttinen P, European Influenza Surveillance Network . Seasonality and geographical spread of respiratory syncytial virus epidemics in 15 European countries, 2010 to 2016. Eurosurveillance. 2018;23(5):17‐00284. doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2018.23.5.17-00284 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

