Association for Human Pharmacology in the Pharmaceutical Industry conference 2022: impending change, innovations and future challenges
- PMID: 38026971
- PMCID: PMC10651721
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1219591
Association for Human Pharmacology in the Pharmaceutical Industry conference 2022: impending change, innovations and future challenges
Abstract
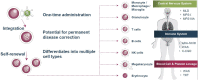
The Association for Human Pharmacology in the Pharmaceutical Industry's annual meeting focused on current and impending challenges facing the United Kingdom's (UK) pharmaceutical industry and how these opportunities can inspire innovation and best practice. The UK pharmaceutical landscape is still evolving following Brexit and learnings from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. As such, the UK's clinical community is in a unique position to steer innovation in a meaningful direction. With the continuation of remote forms of working, further opportunities have arisen to support novel practices away from the clinic. The keynote speaker reflected on clinical development over the past 40 years and how the industry must continue to concentrate on patient welfare. The future of drug development was discussed regarding challenges associated with developing translational gene therapies, and the status of investment markets analyzed from a business strategy and consulting perspective. The patient viewpoint was a core theme throughout the conference with patient-centric blood sampling and decentralized clinical trials providing suggestions for how the industry can save costs and increase efficiency. Moreover, the patient perspective was central to a debate over whether ethics requirements should be the same for oncology patients taking part in first-in-human studies as those for healthy subjects. Discussions continued around the changing roles of the Qualified Person and Principal Investigators which underpins how sponsors may want to run future trials in the UK. Lessons learned from conducting challenge trials in healthy volunteers and patients were discussed following a presentation from the serving Chair of the COVID-19 challenge ethics committee. The current state of interactions with the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency were also explored. It was considered how the immediate future for the UK clinical trials community is inevitably still linked with Europe; the newly implemented European Medicines Agency Clinical Trials Information System has been met with lukewarm responses, providing a promising opportunity to ensure UK Phase I units continue to play a vital role in global research.
Keywords: association for human pharmacology in the pharmaceutical industry; drug development; early phase clinical development; innovation; meeting report.
Copyright © 2023 Mundy, Bush, Cheriyan, Lorch, Stringer, Taubel, Wydenbach and Hardman.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors CM and TH were employed by Niche Science & Technology Ltd. Author JB was employed by Covance Clinical Research Unit Ltd. Authors UL and JT were employed by Richmond Pharmacology Ltd. Author SS was employed by Alwyn Consulting. Author KW was employed by Weatherden Ltd. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Association of Independent Clinical Research Contractors (1989). Guidelines for research ethics committees. Oakland, CA, USA: AICRC.
-
- Association of the British Pharmaceutical Industry (1970). The report on medical experiments in staff volunteers. Oakland, CA, USA: AICRC;
-
- Association of the British Pharmaceutical Industry (1977). Guidelines for preclinical and clinical testing of new medicinal products. Oakland, CA, USA: AICRC.
-
- Association of the British Pharmaceutical Industry (1988a). Guidelines for facilities for non-patient volunteer studies. Oakland, CA, USA: AICRC.
-
- Association of the British Pharmaceutical Industry (1988b). Guidelines for medical experiments in non-patient volunteers. Oakland, CA, USA: AICRC.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

